Ginger Farming in India: Varieties, Cultivation Process & Production

Ginger, also known as “Adrak”, is one of the most essential spices in India. It is a valuable cash crop and widely used in food, beverages and medicines. Ginger farming in India has significant potential due to its high culinary demand, that is why it is cultivated in almost every state. If you want to start ginger farming, then continue reading this blog to learn the step-by-step ginger cultivation process, along with popular ginger varieties and the major producing states.
Table of Contents
- Ginger Farming in India: An Introduction
- Which are the Popular Ginger Varieties in India?
- Ginger Cultivation Practices in India
Ginger Farming in India: An Introduction
Ginger is an herbaceous perennial crop, grown for its rhizomes, which are used as a spice. It is known for its warm, pungent and sweet-spicy taste. The scientific name of ginger is “Zingiber officinale”. It is used in various forms, including raw ginger, dry ginger, ginger powder, ginger oil, ginger oleoresin, ginger ale, and ginger candy. It is also used in herbal teas due to its vast potential health benefits. It also aids in digestion, alleviates nausea, and helps combat the common cold. India is the world's largest producer of ginger. It is cultivated in almost all states in India, which ensures an abundant supply throughout the year. Thus, it increases domestic consumption and international export demands, primarily driving the market growth.
Which are the Popular Ginger Varieties in India?
- China
- Assam
- Maran
- Himachal
- Nadia
- Kuruppampadi
- Rio-de-Janeiro
- Mahima
- Ernad
- Wayanad
Ginger Cultivation Practices in India
Soil & climate, land preparation, planting, irrigation, etc. are the major cultivation steps of ginger. Let’s understand the complete step by step ginger cultivation process below.
Soil & Climate Requirements
Ginger crop grows best in well drained soils like sandy loam, clay loam, red loam or lateritic loam. The ideal pH range of ginger is 5 to 7.5. It requires humid climate and a temperature range of 19°C to 28°C and a humidity of 70-90%. It is cultivated from sea level to an altitude of 1500 m above sea level. It can be cultivated both under rainfed and irrigated conditions.
Land Preparation
Plough the land 4 to 5 times to a fine tilth. Prepare the beds of 1 m width, 15 cm height and of convenient length with an interspace of 30-50 cm in between beds. Raise bars with 40 cm intervals if irrigation facilities are provided.
Seed Selection & Treatment
Select the right quality seed rhizomes and preserve them properly free from pests and diseases. Ginger is propagated by seed tubers. Seed tubers that have 2.5 to 5 cm in length and weigh from 20 to 25 grams are used to make one or two viable nodes are used in propagation. 1500 to 1800 kg/ha seed tubers need for plains and 2000 to 2500 kg/ha are recommended for hilly areas.
Planting Method
The best season to grow ginger is March to April. The ginger crop duration is generally around 8-9 months (April/May to December/January). It is planted in rows at 30 cm apart at distances of 20-25 cm within the row. The seed rhizomes of 30 to 50 g in weight, 3-5 cm in length and having at least one bud are planted at the given spacing. About 2.0 t rhizome/ha is required for planting one hectare land. Mulching is done to cover these seeds as protection against sun and heavy rains.
Irrigation & Weed Management
Irrigate the crop immediately after planting. The subsequent irrigations are given at intervals of 7 to 10 days. Sprinklers and drip irrigation system can also be used for better yields. Two weeding are generally given to the crop. The first weeding just before the second mulching and repeated depending on the intensity of weed growth.
Pests & Disease Management
|
Pests & Diseases |
Symptoms |
Control Measures |
|
Stem Borer |
Yellow colour of the leaves, stems drying. |
Spray the pesticide monocrotophos 0.1% (1 liter of water 1 ml) and infested plants should be removed. |
|
Leaf Roller |
Folded and defoliates the leaves from the tips and margins. |
Spray carbaryl 0.1% (1g per liter of water) or dimethoate 0.05% or phosphamidon 0.05%. |
|
Tuber scales |
Dried leaves and reduces the germination capacity. |
Spray phosphamidon 0.05% (5 ml with 10 liters of water) or spray malathion in the bag which is filled with tuber. |
|
Tuber Rot |
Water-soaked lesions in collar region of pseudostem. |
Tubers are treated with Mancozeb or copper oxychloride. |
|
Leaf Spot |
Oval to elongated water-soaked spots will appear on the leaves. |
Application of Bordeaux mixture @ 1% or copper oxychloride @ 0.3% effectively control the disease. |
Harvesting & Yield
The ginger plant is ready to harvest after eight months of planting depending upon the maturity of the variety. The accurate ginger harvest time is when leaves turn yellow and the pseudo-stems begin to dry. The average ginger yield per acre is 15 to 20 tons of ginger rhizomes.
Which are the Major Ginger Producing States in India?
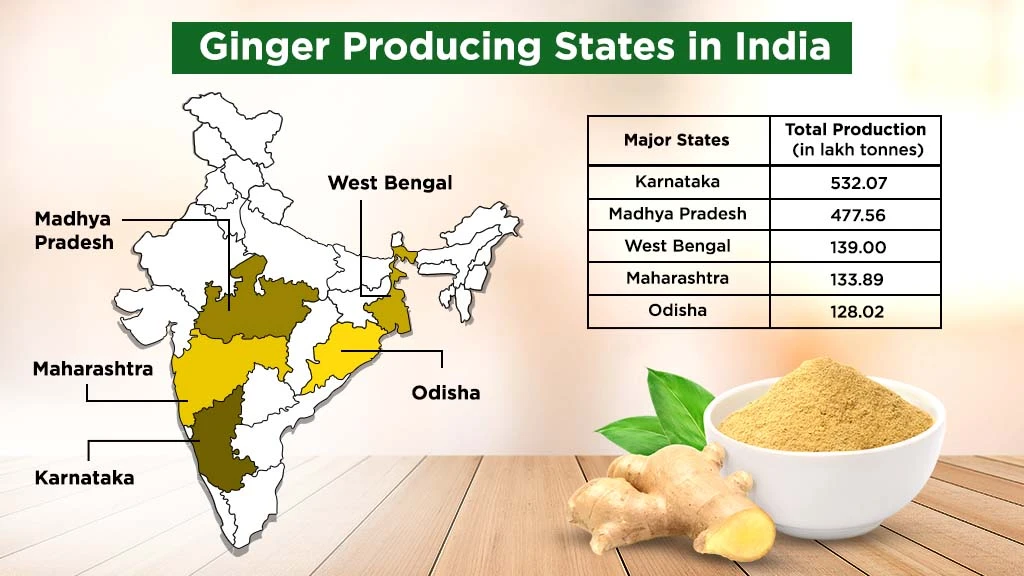
|
Major Ginger Producing States |
Total Production (in lakh tonnes) |
|
Karnataka |
532.07 |
|
Madhya Pradesh |
477.56 |
|
West Bengal |
139.00 |
|
Maharashtra |
133.89 |
|
Odisha |
128.02 |
Frequently Asked Questions On Ginger Farming in India: Varieties, Cultivation Process & Production
1. Is ginger farming profitable?
Yes, ginger farming is a profitable venture for farmers as it provides higher yields and better income to the farmers.
2. How long does it take ginger to grow?
Ginger usually takes 8 to 9 months to grow after planting depending upon the varieties.
3. How much ginger can be grown in 1 acre?
Around 6 to 10 tonnes ginger can be grown in 1 acre which depends upon the ginger varieties.
4. What fertilizer is best for ginger?
The best fertilizer dose for ginger is NPK in 75:50:50 kg/ha ratio.


Related Blogs












