How to Start a Successful Nursery Business in India?

The demand for Horticultural crop, ornamental plants and high-quality seedlings is steadily rising across urban and rural India. This increasing demand for better planting materials has contributed to the success of the nursery business in India. However, starting and managing a nursery involves several steps and requires specialized skills & expertise.
Read on to learn how to start a successful nursery business in India.
Table of Contents
- What is Nursery in Agriculture?
- Which are the Different Types of Nurseries?
- How to Start a Nursery Business in India?
- What are the Documents Required for Nursery License in India?
- Government Support for Nursery Business
What is Nursery in Agriculture?
A nursery is an area dedicated to raising high-quality seedlings and saplings before transplanting them into permanent fields. Nurseries are designed to offer ideal conditions for the propagation and multiplication of planting materials such as seeds, seedlings, and plant cuttings.
They play an important role in horticulture and are also essential in agriculture, for rice, vegetable, sugarcane cultivation through transplanting. There are many advantages of raising a seedling or sapling in a nursery including the capacity to grow a wide variety of plants in a short amount of time, uniform crop development, improved care and management, and higher germination rates.
Hi-tech nurseries are also being introduced where plants are grown in plastic tunnels, glass buildings or greenhouses to provide suitable growing conditions. These modern greenhouses provide provisions for automatically controlling watering, light, ventilation, feeding, and temperature.
Which are the Different Types of Nurseries?
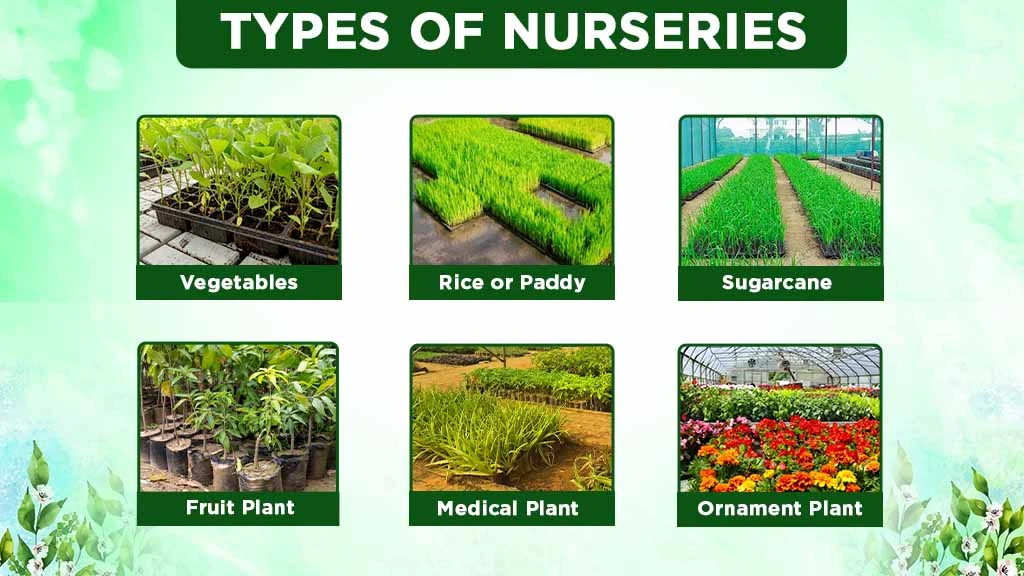
Different type of nurseries based on plants are given below.
Vegetables Nursery: A vegetable nursery is a facility that grows vegetable seedlings from seed until they are large and strong enough to be transplanted onto the main field for farming. These nurseries are designed to grow a wide range of crops from seedlings, such as capsicum, cauliflower, brinjal, and onion. Some exceptions include bulbous vegetables, sweet potatoes, and potatoes.
Rice or Paddy Nursery: A rice nursery is commonly referred to as a rice nursery bed or rice seedling nursery. These areas are especially prepared to grow young rice seedlings before they are transplanted into the main field. This is typically done with the help of a rice transplanter.
The rice beds are typically well-levelled, fertile, and have proper drainage to promote healthy seedling growth.
Sugarcane Nursery: A sugarcane nursery is a specialised facility for propagating healthy and disease-free sugarcane setts (‘stem cuttings’ or ‘sugarcane stalk cuttings’) which are transplanted mechanically with the help of multi crop row planter. Seed sets are often placed in polythene bags or trays and provide adequate watering and fertilisation to promote healthy seedling growth.
Fruit Plant Nursery: The propagation of most fruit crops like oranges, guava, sapota, pomegranate and mango is done through vegetative method. They demand specialized methods for propagation and maintenance. Fruit nurseries are used to produce good quality grafts with the help of rootstocks and quality scions.
Medicinal & Aromatic Plant Nurseries: This nursery type specializes in conserving and multiplying valuable medicinal and aromatic plants. Some of the medicinal plants grown in a nursery are vasaka, sagargota, aloe vera and vetiver lemongrass.
Ornamental Plant Nurseries: There are several ornamental and floriculture crops, including lilies, roses, carnations and gladiolus, that are propagated vegetatively. Many ornamental plants like salvias, marigolds and asters are propagated using seeds and seedlings.
Also, nurseries are classified as follows based on the type of sale:
- Wholesale Nurseries
- Retail Nurseries
- Private Nurseries
How to Start Nursery Business in India?
Site Selection
One of the most important aspects of starting a nursery business is site selection. A plant nursery should be established near marketing centres to ensure convenient and cost-effective transportation of products without damage. The site should also be located close to high-quality soil sources. A reliable water source is essential within the nursery. In some cases, windbreaks or tall plants, such as seedling mango, aonla, and eucalyptus, require to adequate shade and protection.
Soil
Testing of soil samples is important to avoid unsuitable and problematic soils. The ideal soil type should be porous, well-drained, and have a light to medium texture. It is important to avoid sandy, ill-drained, heavy, black cotton or any soil over 8 pH. The ideal soil pH should be between 6.5 - 7.5. The soil must not have harmful elements or be too saline in nature.
Drainage
Good drainage should be established around the nursery and in between the beds. It is good to have a gentle slope on the pot bed surface. Remember to prevent water logging around beds and pots.
Selecting the Right Products
Conducting market studies in nearby areas can also provide valuable insights for targeting a bigger market. A variety of ornamental plants, including flowering plants, shade-loving foliage, and those suitable for gardens, businesses, and residential buildings, can be propagated to meet customer needs.
Seedbed & Nursery Beds
To grow flower seedlings, temporary or permanent seedbed structures should be created. These beds should be raised at least 0.5 to 0.75 meters above ground. The width of the beds can range from 0.75 to 1 meter, with the length depending on the available land space. Additionally, the beds should have a slight slope and proper drainage.
Selecting and Planting Quality Mother Plants
The proper selection and planting of mother plants is an important step in developing a nursery. These mother plants are planted in separate areas, with different varieties allocated to distinct plots. For the best results, consider sourcing quality mother plants from reputable sources such as agricultural universities or government-run nurseries. Careful procurement of these plants is very important, as the quality of mother plant directly influences the success and sales of nursery stock.
Storing Fertile Soil & Compost Manure
During the summer or hot months, dried, cleaned soil and compost are stored until the early winter or rainy season, when flower seedlings are raised. It is difficult to store manure and dry soil during the rainy season. For this reason, if compost is not stored, seedlings cannot be raised throughout the rainy season.
Quality Seed Procurement
Selection of good quality seeds is a highly specialized task and thus needs careful supervision. When the seed quality is good, seedlings' vigour, seed germination rate, and vegetative growth of plants will also be good. After quality seed harvesting and before marketing seeds, it is recommended that seedling vigour and germination percentage be checked.
Storing Propagated Plants
Nursery beds are used to plant the propagated plants for plant hardening or better growth. Usually, such a nursery bed is established in partial shade.
Manuring & Fertilizers
Manuring and fertilization are essential to promote the healthy growth of plants. Pests and insects are a major threat to fruits and flowers. Chemicals like herbicides, insecticides, fungicides and pesticides can be used to manage insects. To promote soil fertility and aeration, mix one-part FYM, one part sand, and two parts fine red earth into each bed. Pathogenic spores can be destroyed before bed preparation by adding 0.3% copper oxychloride or 4% formaldehyde.
Irrigation
Watering is required based on the needs of the plant. There should be a distinct water source in the nursery. A well of 12 m depth X 3 m diameter, along with a 2 HP kerosene pump set, is fit for this model. In the beginning, irrigation using a sprinkler system is not recommended.
Nursery Equipment & Tools
The tools and equipment required for a nursery are essential for performing various operations throughout the seedling raising process, from preparation of beds to uprooting and transplanting of seedlings. Here’s a list of the key tools:
Coco-pits: Used for soil replacement for saplings.
Nursery Bags: Containers used for growing seedlings.
Grafting Knives: Essential for grafting and pruning plants.
Manual Sprayers: Used for applying pesticides, fertilizers, and water.
Miscellaneous Tools: Various other tools necessary for general nursery operations.
Marketing Nursery
Promoting and marketing a plant nursery involves showcasing the different kinds of plants offered while establishing a strong local and online presence. This can be done through various methods such as using social media, word-of-mouth, local marketing, and e-commerce sales.
What are the Documents Required for Nursery License in India?
- Form – I Application Form for Recognition of Horticulture Nursery
- Form – II Verification report by the Deputy Director of Horticulture
- Paid Challan receipts
- LPO (Legal Process Outsourcing)
- Sketch map of the nursery verified by the Revenue Inspector
- Joint verification report from the DDH and Tahasildar
- NOC from land shareholders
- DDH certification that the document is verified
- Affidavit confirming compliance with Nursery Act & Licensing Authority / Competent Director of Horticulture
- Attested registration sale deed
Government Support for Nursery Business
RKVY (Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana)
The RKVY (Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana) project is a comprehensive scheme for the development of agriculture and related sectors in India. Launched in 2007, it encourages states to improve public investment in agriculture and allied fields. This scheme was developed with the goal to achieve 4% annual growth in the agriculture sector, incentivise public investment in agriculture and related industries, and give states flexibility in planning and executing scheme based on local needs.
NHB (National Horticulture Board)
The National Horticulture Board (NHB) scheme for organic farming focusses mainly on promoting and supporting the development of the organic and natural farming industries. The NHB has established a specialised vertical to oversee all areas of organic and natural farming.
MIDH (Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture)
The MIDH (Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture) initiative promotes organic cultivation and certification by providing financial and technical assistance to farmers and organisations. It covers a wide range of horticulture goods, including fruits, vegetables, and flowers, as well as subsidies for operations such as nursery establishment, area development, and the regeneration of older orchards.
National Horticulture Mission (NHM)
The National Horticulture Mission (NHM) was established in 2005 with the goal of developing nurseries for genetically pure plant materials. Nurseries at government establishments (public sector) receive 100% subsidy on expenditures. The private sector receives a 50% subsidy. Financial support of up to 30 lakhs is available for large nurseries spanning one acre. A subsidy of up to 18 lakhs is available for plots measuring one acre. These subsidies are based on sanctioned bank loans. Furthermore, there are different schemes under NHM to establish horticulture nurseries:
- Organic farming
- Irrigation facilities
- Controlled farming
- Establishing new orchards
- Integrated Pest & Disease Management
- Self-employment program
Nursery business in India can help farmers earn additional income. With increasing demand for ornamental and medicinal plants, nurseries are coming up on a large scale. If you are also considering entering this business, make sure to follow the key points mentioned in this guide.


Related Blogs












