Internet of Things in Indian Agriculture: Scope & Applications

IoT (Internet of Things) in agriculture, also called smart agriculture, is the process of using IoT in farming to enhance productivity and efficiency using connected sensors, data analytics, and other devices. Read this blog to learn the various aspects of IoT in Indian agriculture, including its scope, uses, and future prospects.
Table of Contents
- What is Internet of Things (IoT)?
- What is the Role of IoT in Agriculture?
- What are the Applications of IoT in Indian Agriculture?
- Which are the Popular IoT Devices Used in Agriculture?
- Conclusion
What is Internet of Things (IoT)?
The Internet of Things (abbreviated as IoT) is a network of physical objects or things equipped with sensors, software, and several other technologies that allow them to connect and exchange data with other systems and devices over the internet. Its primary goal is to facilitate the automation of processes, increase efficiency, improve decision making, and develop new services by allowing communication and data exchange between the physical object and the digital world.
What is the Role of IoT in Agriculture?
IoT has revolutionized traditional farming practices by integrating technology into Indian agriculture to improve productivity, efficiency and sustainability. Different IoT devices, such as crop monitors, weather monitors, soil moisture sensors, and drones, are now being used across farmlands to collect real-time data on various factors, such as weather patterns, soil conditions, crop growth and equipment performance.
IoT-enabled technological methods in agriculture help access soil health, fertilizer requirements, soil erosion, soil fertility status, and crop quality. It also helps with optical irrigation, seed quality, and surveillance of crop growth at different stages. Real-time data obtained from remote sensing and IoT can be used for precision agriculture and forestry.
What are the Applications of IoT in Indian Agriculture?
The adoption of IoT in agriculture can help improve the farm’s competitiveness by increasing efficiency, quality, and sustainability, fulfilling regulatory needs, and satisfying customer demands. The various uses of IoT in the Indian farming sector are discussed below:
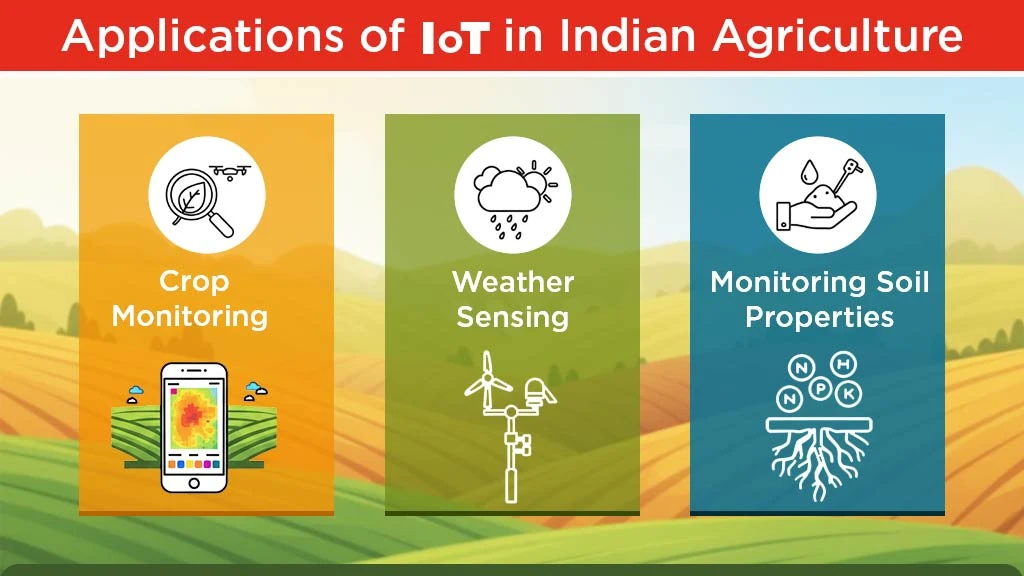
IoT for Crop Monitoring
The IoT-based technology allows farmers to monitor crop growth and health precisely. It helps farmers assess crop disease and pest attack in real time. The IoT-tagged sensors offer real-time data that help farmers and researchers manage crop cultivation, irrigation, fertilizer applications, and plant surroundings smartly.
IoT sensors are employed on the farms to collect information regarding temperature, soil moisture, humidity, and nutrient levels. These are the primary components of IoT-based smart crop monitoring systems. These IoT sensors are networked frequently, providing real-time data transmission to a centralized cloud-based platform. It provides insights into plant health and its growth and yield potential. Farmers can use this information to make choices on crop management, such as pest control, irrigation, and harvest.
IoT for Weather Sensing
IoT can sense different parameters of weather, such as temperature, humidity, and soil moisture. IoT with smart sensors and a wireless network offers real-time data on environmental factors, which helps in more precise farming in vineyards. If there are some changes in the essential environmental factors beyond the threshold level, then IoT sends alarm to the administration to take the required action against the forthcoming adversities. It also has surveillance on CO2 content, humidity, luminance, and temperature for the growth of plants in real time.
IoT for Monitoring Soil Properties
IoT technologies equipped with smart sensors can monitor different soil aspects essential for crop growth. It can sense temperature, soil moisture, and nutrient content. This information can be calibrated and used by farmers to take proper precautions against pest attacks and crop diseases. It also allows farmers to track the pH of the soil and rhizosphere zone multiparameter from remote regions to take preventive measures.
Which are the Popular IoT Devices Used in Agriculture?
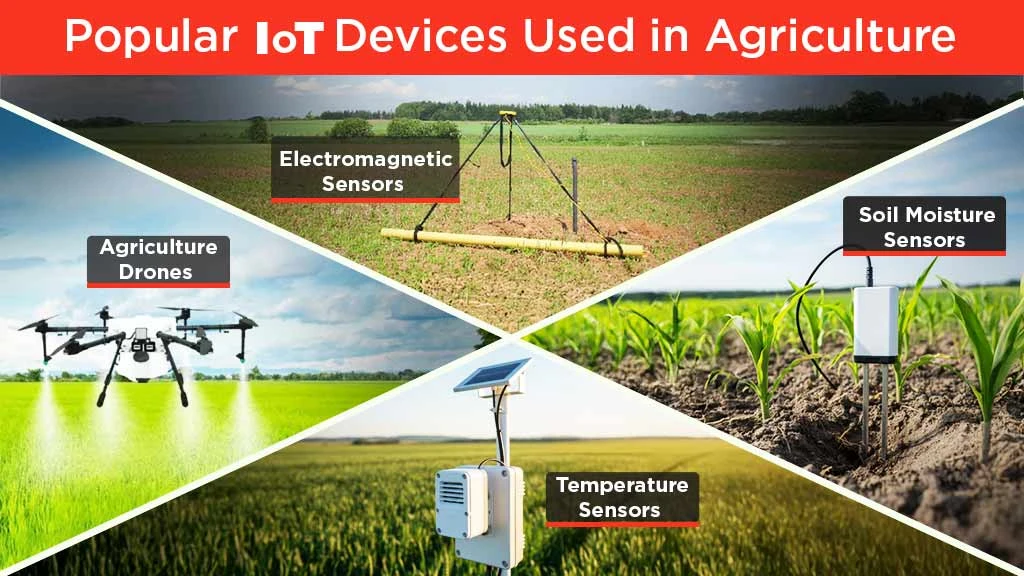
The popular IoT devices used in agriculture are discussed below:
Soil Moisture Sensors
It processes the water contented in soil. It is used to detect data about water requirements in the soil and for automatic watering the land. It ensures less water usage to grow crops.
Temperature Sensors
These sensors are quite low-cost sensors, having low output impedance and a linear output. These electronic devices are used to monitor the temperature of the soil. Soil temperature is a crucial aspect as it affects respiration, photosynthesis, transpiration, the soil’s water potential, and microbial activity.
Agriculture Drones
Agriculture drones can revolutionize manual activities in farming. Using different sensor configurations can help measure land sizes accurately, classify crop types and varieties, produce soil maps, and apply effective pest management strategies. Drones can be used for water stress monitoring, crop health monitoring, deficiency monitoring, and nutrient status. They are also used for spraying, seed plantation from the air, etc.
Electromagnetic Sensors
These sensors are useful in detecting agriculture soil and contamination. They can detect a large spectrum of waves received from different objects. Ground penetrating radar and electromagnetic induction have been involved in estimating soil-water content. Additionally, these sensors can measure organic matter concentrations in soil, residual nitrate levels, and real-time measurement of transpiration rate.
Conclusion
IoT in agriculture is revolutionizing the way farming is done in India by using technology to reduce input costs, environmental impact, and improve efficiency, productivity, and the overall sustainability of farming operations. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is currently among the fastest-growing technologies. It is now being used in different industries, ranging from robotics development to environmental issues monitoring. It has been mediated by automation in different sectors and AI in agriculture is now being adopted by farmers for more efficient farming. AI with smart sensors is now being used in agriculture that has made the IoT more advanced. Using IoT in agriculture is quite helpful for farmers as it makes crop monitoring easy, anytime, anywhere.
Frequently Asked Questions On Internet of Things in Indian Agriculture: Scope & Applications
1. What is the role of IoT devices in agriculture?
The role of IoT devices is to revolutionize traditional practices in agriculture by integrating technology into Indian agriculture to improve productivity, efficiency and sustainability.
2. What are the risks of IoT in agriculture?
The major risks of IoT in agriculture are cyber security threats like data breaches, system hijacking, and sabotage, that can result in financial losses and disruption of operations.
3. What are the 5 C's of IoT?
The 5 C’s of IoT are connectivity, continuity, compliance, coexistence, and cybersecurity.
4. How many types are there in IoT?
The popular IoT devices are soil moisture, temperature, and electromagnetic sensors, and agricultural drones.


Related Blogs












