Coconut Cultivation in India: Top Varieties and Major Producing States

Coconut is also known as “Kalpavriksha” (tree of heaven), originated in the Southeastern parts of Asia. It is a widely known edible fruit of the coconut palm tree. India is one of the largest producers of coconut in the world. In today’s blog, we will understand the complete process of coconut cultivation, along with its top varieties and major coconut-producing states in India.
Table of Contents
- An Overview of Coconut Farming in India
- What are the Benefits of Coconut Farming?
- Which are the Top Varieties of Coconut in India?
- What is the Cultivation Process for Coconuts in India?
- Which are the Major Coconut Producing States in India?
- Get Information regarding the Popular Farm Machinery used in Coconut Cultivation from Tractorkarvan
An Overview of Coconut Farming in India
Coconut production is vital for India’s economy. Its scientific name is “Cocos Nucifera”. The farmers in India grow coconuts in large numbers in their coconut farms, so coconuts are one of the sources of their livelihoods. According to the Coconut Board of India, the total coconut production in India accounted for 21,373.62 million nuts in 2023-2024. There are many uses of coconuts in India, including food, soaps, hair oils, cosmetics, food and beverage, medicines, fuel, and roofing. Moreover, ropes, mats, brushes, mattresses, and other items are also made from the coconut husk. Coconut flour, coconut milk, and coconut oil are eaten in its natural state. In some regions of the country, the tree’s sap is used to manufacture sugar, jaggery, and traditional beverages. As we have got an idea of its uses, let’s have a look at the benefits of coconut.
What are the Benefits of Coconut Farming?
- All Year-Round Crop: Coconut is a long-term crop which can live up to 100 years. So, it provides all the benefits to the farmers throughout the year.
- Low maintenance: It is a low maintenance crop which can grow in all seasons. It requires less irrigation facilities, less manure & fertilizer and no pruning.
- Generate Employment Opportunities: Many people in rural India uses coconut husks to make ropes and brooms which create income opportunities for them.
- Intercropping: As it is a long-standing crop there is enough space to grow other crops such as cocoa, banana, pineapple, pepper, betel leaf etc. which gives benefit of planting these crops and further give additional income to farmers.
Which are the Top Varieties of Coconut in India?
There are three varieties of coconut, namely tall, dwarf, and hybrid varieties. Let’s have a look at each of the following varieties below:
|
Tall Varieties |
Dwarf Varieties |
Hybrid Varieties |
|
West coast tall |
Chowghat Orange Dwarf |
Kerasankara |
|
East coast tall |
Chowghat Green Dwarf |
Chandrasankara |
|
Chandrakalpa |
|
Chandralaksha |
|
Kerachandra |
|
Keraganga |
|
Kera Sagara |
|
Lakshaganga |
|
Aliyar Nagar 1 |
|
|
What is the Cultivation Process for Coconuts in India?
The cultivation process of coconuts requires proper care and maintenance. Let’s look at the important factors and understand how to plant a coconut tree by following several steps.
Soil and Climate Requirements
Coconut best grows in red sandy loam, alluvial, and laterite soils with a minimum depth of 1.2 m and good water-holding capacity. Coconuts can be grown in soil with a pH of 5.2 – 8.6. The climate with high humidity is ideal for the coconut; however, it is a perennial crop. The temperature requirement is 27°C with 5-7°C diurnal variation.
Land Preparation
The planting holes for coconut planting should be marked in appropriate spaces. If the land is sloppy, it is important to adopt soil conservation methods. In hilly regions, contour terracing or bunding should be adopted. If the groundwater level is high, the planting should be done in mounds. In low-lying areas and rice fields, mounds are formed to a height of at least 1 m above water level.
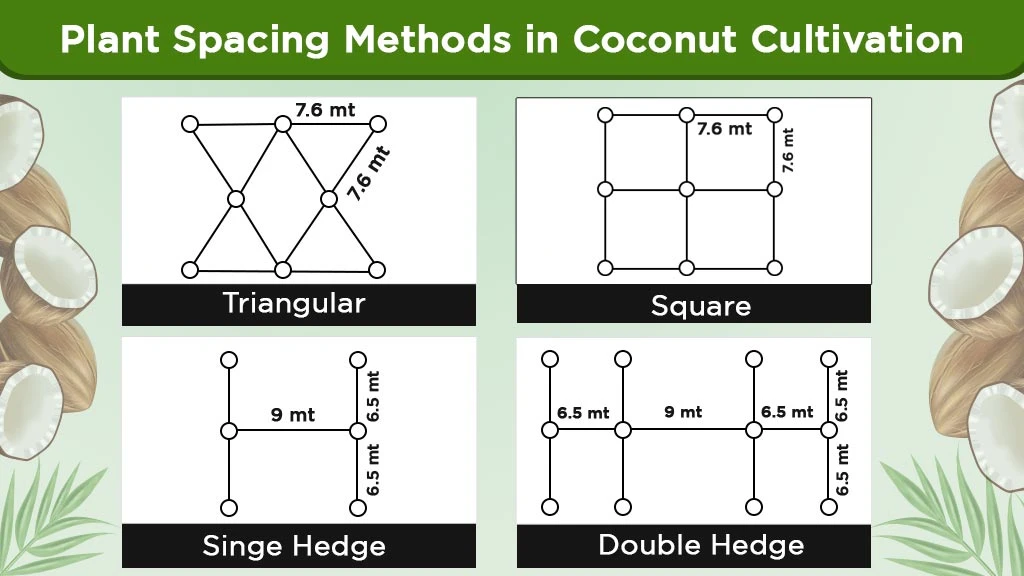
Plant Spacing Pattern
There are different plant spacing patterns according to the variety, such as tall, dwarf and hybrid. Spacing of 7.5 x 7.5 m with 175 plants/ha is ideal for tall varieties, whereas a spacing of 8.5 x 8.5 m is optimum for hybrids. A dwarf variety needs a spacing of 6.5 x 6.5 m, followed by 20 ft. spacing between plants for planting in the field border as a single row.
There are four methods of plant spacing, which are as follows:
- Triangular Spacing
- Square Spacing
- Single Hedge Spacing
- Double Hedge Spacing
|
Planting System |
Spacing |
Approximate number of plants/ha |
|
Triangular |
7.6 m |
198 |
|
Square |
7.6 to 9 m (7.6 x 7.6 m, 8 x 8 m, 9 x 9 m) |
170-120 |
|
Single Hedge |
5 m in the rows, 9 m between the rows, or 6.5 m in rows – 9 m between rows |
220 |
|
Double Hedge |
5 x 5 m in rows, 9 m between pairs of rows, or 6.5 to 6.5 m in rows – 9 m between pairs of rows |
280 |
When a hedge planting pattern is followed, the rows should be aligned in a north-south direction, and the seedlings should be planted as in the triangular system.
Planting
May to July is the ideal planting season for coconuts. Follow the steps below to plant the best coconuts:
- Based on the selected plant spacing method, dig the pit of 3 X 3 X 3 ft. and fill it with FYM at a height of 2 ft. Fertilizer with 500:320:1200 g N, P2O5, and K2O per palm per year is recommended.
- The coconut seedlings are planted in the center of the pit. Two layers of coconut husk (with a concave surface facing up) can be arranged at the bottom of the pit before filling up. This will help in conserving the moisture.
- Regular manuring is important after the first year of planting. A 20-50 kg organic manure is required per palm per year with the onset of the southwest monsoon when the soil moisture content is high.
- The coconut tree becomes fruit-bearing in 4-5 years.
- In rain-fed conditions, apply fertilizers in two split doses, 1/3rd at the time of early southwest monsoon showers in April-June and 2/3rd in September-October.
Care of Young Palms
The care of young coconut palms is necessary for their proper growth and development. At the early or young stage, the palms need special care and attention to become fruit-bearing without any difficulty. Consider the following points:
- Coconut palms should get enough water. For the first two years from planting, irrigate @ 45 litres of water per seedling, once in 4 days, during dry summer months.
- Provide proper shading and staking to the palms so that winds may not uproot the young seedlings.
- The young palms of coconut should also be protected from pests and weeds.
- Moreover, fencing is needed to protect them from animals.
Intercropping
Always choose the crops for intercropping based on the climatic conditions, soil type and irrigation facilities. The other points to be considered are canopy size, age and spacing of the coconut. The following are the best crops for intercropping based on the age of the coconut:
- Early Stage: Turmeric, banana, and sesame are the best crops to grow as intercrops with coconut at the early age of below 5 years. Avoid crops like paddy and sugarcane.
- Young Stage: The different types of grasses, like Napier grass and guinea grass, are the best options as intercrops with coconut in this stage. This is the period of typically 5-20 years of age.
- Adult Stage: Depending upon the soil and climatic suitability, the cocoa, pepper and nutmeg are the best intercrops in the adult stage.
Weed Management
- Keep the pits free from weeds with the help of power weeder. Remove the soil if the seedlings are covered with collars. As the seedlings grow and form stems, fill up the pits gradually by cutting the sides.
- Proper inter-cultivation also helps control weeds and creates soil mulch.
- The interspacing should be ploughed twice in a year.
Pest and Disease Management

|
Pests and Diseases |
Symptoms |
Control |
|
Rhinoceros Beetle |
bore into unopened fronds and spathes. The attacked frond, when fully opened, shows a characteristic triangular cut. |
Naphthalene balls 12 g (approx. 4 nos) in innermost 2 leaf axils at 45 days interval. |
|
Coconut Eriophyid mite |
Mite infests on the meristematic tissues under the perianth. Initial symptoms are exhibited as triangular pale white or yellow patches close to the perianth. |
Apply 1% Azadirachtin, i.e. 4 ml in 1 litre of water. |
|
Bud Rot |
yellowing of one or two younger leaves. |
Spray 0.25% Copper oxychloride or 1 % Bordeaux mixture on the crown of the neighbouring palms as a prophylactic measure before the onset of monsoon. |
|
Root wilt (or) Kerala wilt disease: Phytoplasma |
Tapering of terminal portion of the trunk and reduction of leaf size. |
Magnesium may be supplied @ 500 g MgO per palm per year. |
Harvesting
Coconuts become mature in 11-12 months. However, the harvesting time may vary from area to area. 11 months old nuts are used for the main coconut products like coconut oil, food, etc., and further is used in the manufacturing of coir fibre. Usually, the nuts are harvested 6 to 10 times a year. The coconut plant lasts for around 65 years. Ripen coconuts are a good source of all the coconut products. Skilled personnel are traditionally employed to harvest coconuts. They climb to the top of the tree using proper safety devices for harvesting nuts.
Which are the Major Coconut Producing States in India?
According to the Coconut Development Board of India, following are the major coconut-producing states in terms of production and area in 2023-24:
|
States |
Production (Million nuts) |
Area (thousand Ha) |
|
Karnataka |
6,151.00 |
564.62 |
|
Tamil Nadu |
6,091.98 |
492.61 |
|
Kerala |
5,522.71 |
765.84 |
|
Andhra Pradesh |
1,707.08 |
107.37 |
|
West Bengal |
421.18 |
32.93 |
|
Others |
1479.67 |
201.83 |
|
Total |
21,373.62 |
2,165.20 |
Get Information regarding the Popular Farm Machinery used in Coconut Cultivation from Tractorkarvan
Tractorkarvan can help you get information regarding the best farm machinery used in coconut cultivation. Various implements are needed during the coconut cultivation process, such as post hole digger needed during plantation in large scale coconut farming, power weeder and power tiller for weeding purposes, and for crop residue management, a shredder is required to shred the coconut husks. The best part is that all these implements are listed on Tractorkarvan to help you choose the right one and buy it from the market. If you want to learn about implement loans, we have a separate page for it, so you can get details from there. Moreover, stay tuned with Tractorkarvan to get all the updates related to agriculture and farm machinery.
Frequently Asked Questions On Coconut Cultivation in India: Top Varieties and Major Producing States
1. Is coconut farming profitable?
Yes, coconut farming is profitable for Indian farmers as it requires minimum capital for maintenance and gives good returns.
2. How to control weeds in coconut farms?
Weeds can be controlled in coconut farms by periodic weeding and inter-cultivation practices.
3. How long will a coconut plant last?
The lifespan of a coconut plant is around 65-100 years.
4. How to start coconut farming in India?
You can start coconut farming by adopting the best cultivation practices, such as choosing the right soil and climatic conditions, plant spacing pattern, variety, planting, intercropping methods, weed management, etc.


Related Blogs












