
Table of Contents
- Crop Profile & Benefits of Banana
- What are the Different Varieties of Bananas in India?
- How to Grow Bananas and Maximize Yield?
- Cost Benefit Analysis of Banana Cultivation
- What are the Top Banana-Producing States in India?
Crop Profile & Benefits of Banana
The history of bananas can be traced back to South-East Asia across its humid tropical regions. India is considered one of the main centres of origin of this popular fruit. Banana is scientifically known as Musa, and for centuries, it has been an essential part of Indian agriculture. Banana is a perennial herb with trunk-like pseudostem made of leaf sheaths.
Banana is known for its low price and high nutritive value. It is consumed in fresh or cooked form both as ripe and raw fruit. Banana is a good source of carbohydrates and is rich in Vitamin B, magnesium, calcium, phosphorus and potassium. Banana powder is a good first baby food due to its nutritive value.
Banana is also a key ingredient in a wide range of processed products, like banana chips, jelly, jam, puree, wine, halwa and juice. Plantains and their tender stem are cooked as vegetables. Banana leaves are used to make hygienic eating plates, while banana fibre finds use in making items like wall hangers, pots and bags.
What are the Different Varieties of Bananas in India?
Bananas are commercially divided into two types: culinary and dessert. The culinary types produce starchy fruits, which are used as vegetables in the mature unripe form. The most important varieties of bananas in India are:
- Robusta
- Dwarf Cavendish
- Rasthali
- Poovan
- Nendran
- Red Banana
There is an imported variety from Israel, Grand Naine, which is becoming popular in India because of its good quality bunches and tolerance to abiotic stresses. Compared to other cultivars, it has a better shelf life and quality with an attractive uniform yellow colour.
How to Grow Bananas and Maximize Yield?
The primary aim of this section is to offer a reliable model for high-quality commercial cultivation of bananas. Here’s a comprehensive guide for you to grow bananas successfully and maximize your harvest and profits.
Soil & Climate
Banana is a tropical crop and a temperature range of 15°C – 35°C is ideal for its healthy growth with relative humidity of 75-85%. Based on the variety, it is being grown from dry mild subtropics to humid tropical climates in India. The monsoon months from June to September are considered the best months for the vigorous vegetative growth of bananas, with an average rainfall of 650-750 mm. High wind velocity of more than 80 km /hr can damage the crop.
Deep, rich, loamy soil is best suited for banana cultivation. A soil which is rich in organic material, high nitrogen content, and a good amount of phosphorus and potash is suitable for the crop. The ideal soil pH range is 6 – 7.5. Bananas do not grow well in saline, solid, calcareous soils.
Land Preparation
Daincha and cowpea are some green manuring crops that can be grown before planting bananas. Ploughing the land 2 to 4 times and levelling is required. For breaking the clod and forming fine tilt, implements like rotavators and harrows are used. About 50 tonnes/ha of basal dose of FYM should be thoroughly mixed into the soil before the last harrowing.
Ratoon Management
Being a perennial crop, bananas provide succeeding generations of crops. After planting, the first cycle is known as the plant crop. The harvested plant is succeeded by the sucker called the ratoon or the follower. The first ratoon crop comes in the second cycle, while the second ratoon crop is obtained in the third cycle.
It is important to prevent weed infestation in the field and surrounding area. The field must be kept free of weeds to prevent contamination. This is why ratoon management plays a key role in banana cultivation. It involves the selection and nurturing of new growth or suckers after harvesting the first crop. It facilitates the production of a second crop and maximizes banana yield. Three ratoons are done in places like Theni in 24 to 25 months. After emerging of flowers and the full opening of the fruits, a skirting bag is used to cover the bunches. It not only maintains uniform temperature inside but also protects the tender fruits from insect attack.
Planting Method

Banana propagation is done using suckers and rhizomes. Another popular method is tissue cultured plantlets, which is being adopted on a large scale. Sword suckers weighing around 450-700 gm are common propagating material. The tissue culture can be done throughout the year except when the temperature is too high or too low. To treat planting material, its roots and base can be removed. Before planting, suckers can be dipped in a 0.5 % monocrotophos and 0.1% bavistin solution.
The ideal season for planting is May-June or September-October. The cultivation method involves planting a sucker in small pits in an upright position while a 5 cm pseudostem is left above the soil level. During planting, 25 g Pseudomonas fluorescence per plant should be applied. There are three systems of planting generally involved in banana cultivation.
|
Planting System |
Planting Distance |
Plant Population/hectare |
|
Square system |
1.8 x 1.8 m |
3025 |
|
Paired row |
1.2 x 1.2 x 2 m |
5200 |
|
Triangular system |
1.5 x 1.8 m |
3630 |
|
2 suckers/hill |
1.8 x 3.6 m |
3200 |
|
3 suckers/hill |
1.8 x 3.6 m |
4800 |
There are three common methods of planting:
- Pit Method: The size of pits is noted to be 60 cm x 60 x 60 cm x 60 cm, which are filled with a mix of FYM, soil and sand in a 1:1:1 ratio. The soil around the planted suckers is compacted.
- Furrow Method: It involves forming 30-40 cm deep furrows after land preparation. It is done manually or using a ridger. Suckers are planted at suitable spacing with FYM applied around them.
- Trench Planting: In this method, water is used to prepare the field. After draining the water, suckers are planted by simply pressing them into the wet field.
Irrigation & Fertilizer Management
The water requirement of the crop is noted to be 1,800 – 2,000 mm per annum. During summer, irrigation is required at a 4-5 days interval, while it is 7-8 days for winter. Overall, around 70 to 75 irrigations are provided to the banana crop. The plant growth gets impacted if the temperature drops below 10°C during winter. In such a condition, irrigation should be done at night.
Drip irrigation is an effective irrigation method for saving water and increasing yield. It needs to be provided at 15 litres per plant per day from planting to the fourth month. From the fifth month to the shooting stage, it increases to 20 litres per plant per day. From the shooting stage to 15 days before harvest, it goes up to 25 litres per plant per day.
Banana demands a high amount of nutrients from the soil. Its nutrient requirement per plant is as follows:
- FYM (10 kg)
- Nitrogen (200 – 250 gm)
- Phosphorus (60-70 gm)
- Potassium (300 gm)
Banana needs 7-8 Kg Nitrogen, 0.7-1.5 Kg Phosphorus and 17-20 Kg Potassium per metric ton yield. A bunch forms easily during winter with the application of 1 kg neem cake per plant.
Fertigation is a process or a method that is widely used by farmers. It is the method of applying fertilizers and other water-soluble products required by the plant during the initial stages through drip irrigation. It is valuable in mitigating nitrogen loss via leaching, volatilization and evaporation. Also, it avoids the loss of phosphorus and potassium due to soil fixation. It may also improve nutrient efficiency by applying them closer to when the plant needs them.
Intercultural Operations
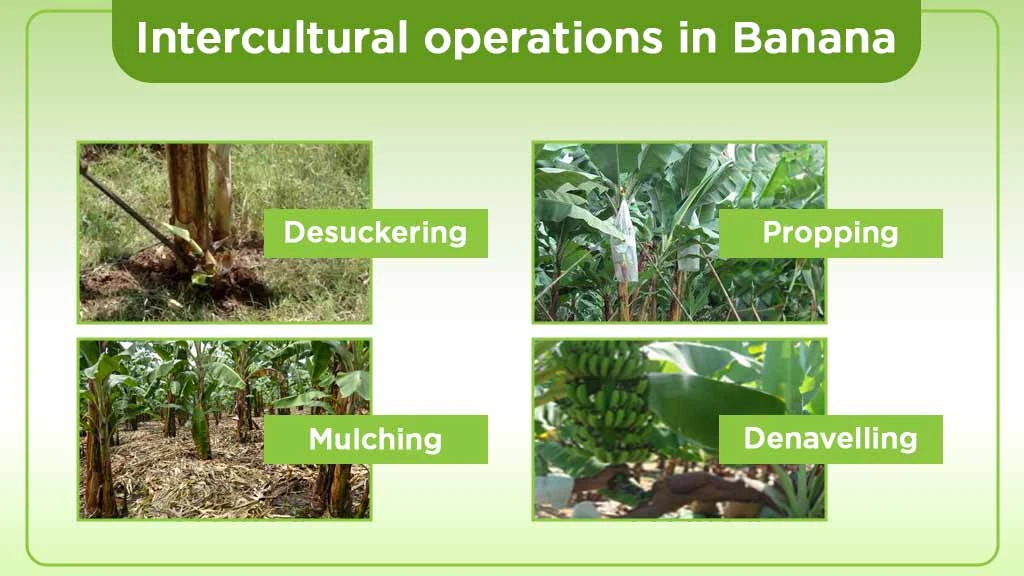
Some intercultural operations are practiced for the better development of the banana crop. The following inter-cultural operations are recommended for optimum productivity of the crop:
- Weeding: During the first four months, there is a need for regular weeding to control and suppress weed growth. It involves spading, use of cover crops, herbicides and intercropping.
- Desuckering: Removal of unwanted suckers from banana plants is known as desuckering. It is important in reducing the competition from the mother plant. Small suckers are removed regularly for up to 7-8 months.
- Propping: Propping basically means supporting the bearing plant. Propping can be done with suitable propping material like bamboo or wooden poles for the uniform development of the bunch.
- Mulching: Mulching is important in the conservation of soil moisture. It enhances the yield productivity in banana crops. The mulch is applied at the beginning of summer (February).
- Denavelling: Removal of the male bud after completion of the female phase is known as denavelling. It helps in promoting the growth of the fruit.
Pest & Disease Management

Some major pests and diseases harming the banana crop are leaf spot, bunchy top, nematodes and rhizome weevil. Neem cake and dasparni arka can be applied to manage pests or diseases in organic farming. Dasparni arka is prepared by mixing 25 kg neem leaves with 2 kg leaves (each) of drumstick, gudwel, karanj, castor, papaya, cotton, kaner, nirgudi and custard apple. It is added to 200 litre water, 2 kg green chillies and 5-10 litre gomutra. The solution is fermented for 15 to 20 days. It is filtered through muslin cloth to prepare a stock solution. 100 litre of water is added to 2.5 litre of arka to dilute the arka, and then spraying is done.
Harvesting & Yield
The harvesting method depends on the plant's height. Harvesting low-growing varieties involves cutting through the bunch stalk around 30 to 35 cm above the top hand. In taller varieties, the plant stem is cut partly to bring the bunch down within the reach of the cultivator.
Based on market preferences, harvesting is done when the fruit matures slightly or fully. At 75-80 % maturity, harvesting is done for long-distance transportation. After 11-12 months of planting, the crop is ready for harvest. After 18 to 10 months of harvesting of the main crop, the first ratoon crop is ready. The second ratoon gets ready after 8 months of harvesting the first ratoon crop. In 27 to 30 months, three crops (one main crop and two ratoon crops) can be harvested.
Cost Benefit Analysis of Banana Cultivation
This economic model pertains to banana cultivation in a 7.5-acre field. The total number of plants in this project is 9259, which are bought at a rate of Rs. 10/plant. If we consider plant mortality, around 8700 plants will grow, offering a total production of 219900 at a yield per plant (kg) of 25. The selling rate is assumed to be Rs. 15/plant. A farmer can easily earn a gross profit of more than Rs. 7.5 lakhs in the first year.
Note that this analysis assumes several rates based on market research and historical data, so the profitability may differ based on market conditions and region. For instance, the land is preowned by the farmer in this project report.
|
Costs |
|
|
Plantation Expenses |
|
|
Cost of planting material |
92590 |
|
Fertilizer & Pesticides |
396000 |
|
Plastic Mulching |
96000 |
|
Cost of Labour |
1016000 |
|
Power & Fuel Expenses |
98000 |
|
|
|
|
Irrigation |
|
|
Cost of Drip/Sprinkler |
188000 |
|
Tube Well & Pump Set |
230000 |
|
Infrastructure & Land Development |
|
|
Fencing, levelling etc |
206000 |
|
Farming Equipment |
38000 |
|
Labour Quarter/Storeroom |
150000 |
|
Total Expenses |
2510590 |
|
|
|
|
Income |
3298500 |
|
Profit |
787910 |
What are the Top Banana-Producing States in India?
India leads the world in banana production. In 2023-24, the total banana production of India was 37.61 million MT. The top banana-producing states in India are:
|
State |
Production in (000) tonnes |
% Share |
|
Maharashtra |
6,534.35 |
17.37 |
|
Andhra Pradesh |
5,830.93 |
15.50 |
|
Tamil Nadu |
4,719.95 |
12.55 |
|
Uttar Pradesh |
4,191.85 |
11.14 |
|
Gujarat |
4,010.72 |
10.66 |
|
Karnataka |
3,121.97 |
8.30 |
|
Madhya Pradesh |
2,453.83 |
6.52 |
|
Bihar |
1,919.98 |
5.10 |
|
West Bengal |
1,440.01 |
3.83 |
|
Assam |
1,022.51 |
2.72 |
Banana is one of the most popular and widely consumed fruits in India. India has performed tremendously in banana production in the world so far. While banana cultivation is growing in India, it also faces major challenges that hamper its productivity. Nevertheless, the future of banana cultivation seems promising with organic farming methods, improved banana varieties and advancements in agricultural practices.
Frequently Asked Questions On A Step-by-Step Guide to Grow Bananas in India
1. Which state is the largest producer of bananas in India?
Maharashtra is the largest producer of bananas, with a total production of around 6,534 tonnes in 2023-24.
2. In which season banana grows in India?
Banana is planted round the year except during heavy rains and severe winter. Ideal vegetative growth takes place during four months of monsoon (June-September).
3. What is the cultivation cycle of bananas?
The cultivation cycle lasts from 8 to 12 months.
4. What is the lifespan of banana trees in India?
The average lifespan of a banana tree in India is 25 years.
5. Which soil is best for banana cultivation?
Sandy loam soil with a pH of 6 – 7.5 is most preferred for banana cultivation.
6. How much water does a banana plant need?
The total water requirement for the entire banana life cycle of banana plants is around 900-1200 mm.
7. Is banana farming profitable?
Yes, banana farming is profitable because of high market demand and year-round cultivation potential.


Related Blogs












