Potential of Mushroom Farming in India: Types, Prices, and Profit

Mushrooms are fungi that grow on moist surfaces such as wood or other organic matter. Mushroom Farming in India has seen a huge growth due to the rising demand for mushrooms for edible purposes. As a result, the profitability from mushroom farming is potentially high. Let us read the complete blog to learn about the steps involved in mushroom cultivation, the various mushroom varieties, and the economics of the mushroom farming business.
Table of Contents
- What are the health benefits of eating mushrooms?
- Which are the Top Mushroom Varieties Cultivated in India?
- What are the Steps involved in Mushroom Farming?
- What are the factors affecting Mushroom Cultivation?
- What are the Market, Price, and Profits for Mushroom Farming in India?
What are the health benefits of eating mushrooms?
Mushrooms are low in saturated fat and calories, and they also add various micronutrients, phytochemicals, and flavonols to your meal. The potential health benefits of eating mushrooms are:
- Mushrooms help improve gut health as they are a great source of prebiotics. They feed probiotics, which are beneficial bacteria in your gut.
- Mushrooms contain potassium, which is beneficial in maintaining healthy blood pressure levels.
- They are equipped with powerful antioxidants, ergothioneine and glutathione, that may help prevent cancer. Some researchers suggest that eating mushrooms regularly is connected to a lower risk of cancer.
- They have a savoury, also known as umami, taste that can substitute for some of the ground beef in a recipe or stand in for steak in a vegetarian meal. Additionally, they are low in fat and calories and using them as a substitute for meat in your diet can help reduce unhealthy fats.
- Mushrooms are good for your brain. Consuming two servings of mushrooms per week can lower the risk of mild cognitive impairment because of their antioxidant ergothioneine.
- Some mushroom varieties are exposed to UV light when they are grown, which produces Vitamin D. Thus, they help maintain strong bones and support immunity.
Which are the Top Mushroom Varieties Cultivated in India?
The top mushroom varieties cultivated in India are button mushrooms, oyster mushrooms, milky mushrooms, reishi mushrooms, and shiitake mushrooms. Let's discuss them in brief:
Button Mushrooms

Button mushrooms, scientifically known as Agaricus bisporus, are one of the most widely consumed varieties of mushrooms in India. They are identified by their round shape, having white caps and a mild flavour. They can be used in a wide range of culinary applications to prepare mouthwatering dishes. They are grown seasonally and in environment controlled cropping houses. Button mushrooms need 20 – 28 degree Celsius for vegetative growth and 12 – 28 degree Celsius for reproductive growth. The humidity required for the growth of this variety is 80 – 90% with proper ventilation during cropping.
Oyster Mushrooms
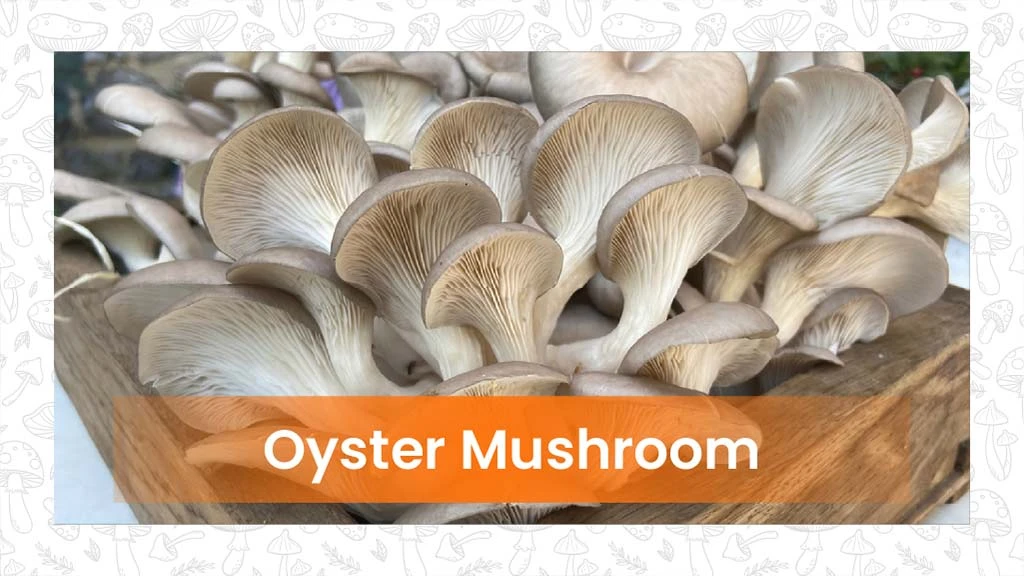

Oyster mushrooms, also known as pearl mushrooms, scientifically classified as Pleurotus ostreatus, are considered one of India's finest mushrooms, offering various health benefits along with a delicate seafood flavour. They are shaped like a fan and dusty colour, and look a lot like oysters. They can be easily grown in tropical and temperate regions and are widely cultivated in the states of Maharashtra, Karnataka, Odisha, West Bengal, etc.
Milky Mushrooms
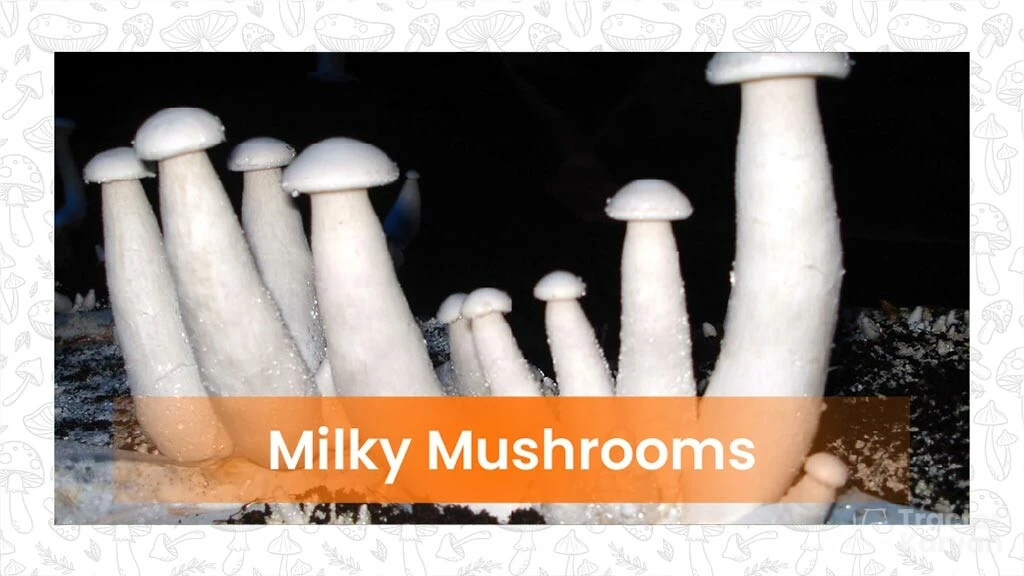

Milky mushrooms, scientifically known as Calocybe indica, can be grown during the summer season when the temperature is high for direct consumption or commercial purposes. They are milky white in appearance, which sets them apart from other types of mushrooms. They are also quite commonly used in preparing a wide variety of dishes and find a special place in the Indian food menu. They are widely grown in states like Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Odisha.
Reishi Mushrooms

Reishi mushrooms, scientifically known as Ganoderma lucidum, have immense medicinal properties. They are known to boost immunity and contain several antioxidants that are good for health. These types of mushrooms are gaining popularity in India's herbal and wellness industries.
Shiitake Mushrooms

Shiitake mushrooms, scientifically known as Lentinula edodes, are added to different dishes for their smoky and rich flavour. They are mainly sourced from East Asia and are now cultivated in various parts of India due to their increasing popularity and market demand. They are used for boosting the immune system, lowering blood cholesterol levels, and as an anti-ageing agent.
What are the Steps involved in Mushroom Farming?
It is important to maintain ideal environmental conditions for farmers involved in its cultivation for healthy growth and improved yield. Button mushroom is the most popular variety cultivated in India, which requires a specific growing environment. Maintaining proper humidity, temperature, and ventilation throughout the cultivation process is critical for the successful production of button mushrooms. Here is the step-by-step process for starting mushroom cultivation.
Spawn Production
The first step in mushroom cultivation is the production of spawns or mushroom seeds. Spawn is a vegetative mycelium culture that is used to inoculate the substrate for mushroom growth. These are produced from either fruiting culture or stocks of selected specimens of mushrooms. These stocks can be grown in a lab, and fruiting culture can be imported from different places.
Composting
The substrate is the material on which mushrooms grow. Generally, substrates include straw, sawdust, compost, or a blend of different organic materials. The substrate is pasteurized before being used to grow mushrooms to eliminate bacteria and competing fungi that could obstruct the growth of mushrooms.
Spawning
Spawning is the process of mixing spawn with compost. There are three different methods of spawning. These are spot spawning, surface spawning and layer spawning. In general, the mushroom seeds are mixed with the whole compost at the rate of 500 – 750 grams per 100 kg compost or 0.75 ml per kg compost.
Casing
After spawning, a casing layer, which is a peat moss or a mix of soil and peat, is spread over to promote fruiting and moisture retention. The casing layer promotes a microclimate for the development of mushrooms.
Cropping
Crop management means maintaining optimal conditions for mushroom growth, which includes regulating temperature, humidity, and airflow. It also includes preventing the crop from pests and diseases to ensure healthy mushrooms are produced.
Harvesting
Different types of mushrooms are harvested at different stages of development. For instance, button mushrooms are harvested when the caps are closed, while oyster mushrooms are generally harvested when the caps begin to flatten. The correct harvesting technique involves gently twisting or cutting the mushrooms to avoid damage.
What are the factors affecting Mushroom Cultivation?
The key factors that affect the growth and development and influence the life cycle of mushrooms and their growth stages are humidity, temperature, and ventilation. Let's discuss them in brief:
Humidity
Mushrooms grow where the humidity levels are high; therefore, it is important to maintain humidity between 80 – 90% for optimal growth of the crop and to prevent drying out the substrate.
Temperature
Different varieties of mushrooms need different temperatures to grow. For instance, Button Mushroom requires a temperature of 24° C for vegetative growth and 16 – 18° C for reproductive growth. Thus, maintaining the ideal temperature is necessary for mycelium colonization, fruiting, and overall production.
Ventilation
Adequate airflow is vital for the growth of mushrooms, as it replenishes carbon dioxide, removes excess humidity, and prevents the buildup of contaminants that can destroy the crop. Proper ventilation leads to healthy mushroom growth and reduces the risk of mould or bacterial infections.
What are the Market, Price, and Profits for Mushroom Farming in India?
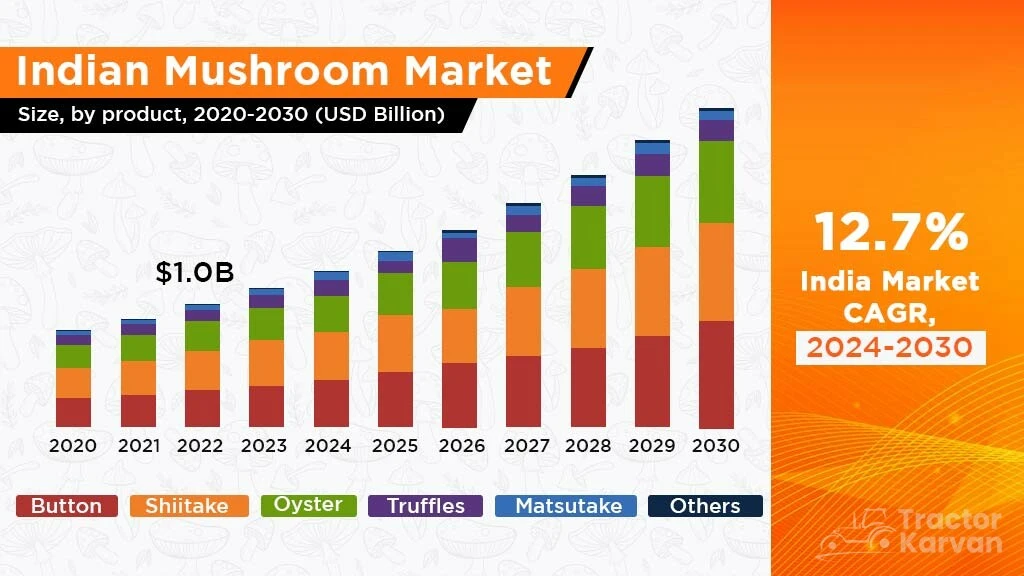
With the rise in demand for mushrooms in India, its market size is experiencing massive growth. As per Businessoffood.in, the market size is expected to reach USD 466.8 million by the end of 2032.
One of the major reasons influencing the demand for mushrooms in India is the mass awareness towards a nutritious diet and the growing vegan population. The seasonal variations highly fluctuate the prices as they influence the yield and availability of mushrooms in the Indian market.
Bihar, Odisha and Haryana are some of the highest mushroom-producing states.
Mushroom farming profit in India is considered to be approximately Rs. 1000 per sq. ft. area. With large-scale production, the upper margin of mushroom cultivation in India is quite high. The profit also varies depending on the area used for farming, the type of mushroom cultivated, and the best market that you find to sell them.
Frequently Asked Questions On Potential of Mushroom Farming in India: Types, Prices, and Profit
1. What are the most common types of mushrooms available in India?
The most common mushrooms found in India are: Button Mushroom, Oyster Mushroom, Shiitake Mushroom, and Reishi Mushroom.
2. Which type of mushroom is the most popular for consumption?
Button mushrooms are considered the best edible mushrooms found in India.
3. Which mushroom is eaten in India?
Button mushroom is widely cultivated and eaten in India.
4. Which city is known as the mushroom city of India?
Solan is known as the city of mushrooms in India.
5. Which state is the largest producer of mushrooms in India?
Bihar is the largest producer of mushrooms in India.
6. Which is the most expensive mushroom in India?
Gucchi, also known as Morel mushrooms, are the most expensive type of mushrooms in India.
7. Is mushroom farming a profitable business in India?
Yes, mushroom is a profitable business in India because with proper management and marketing, a farmer can generate a profit of Rs. 50,000 - 1,00,000 per 1000 bags annually.
8. How big is the Indian mushroom market?
In 2023, the Indian mushroom market size was estimated at USD 1.18 billion, and it is now estimated to reach USD 1.33 billion in 2024 as per Grandview Research.
9. Who are the key players in the Indian mushroom market?
Agro Dutch Industries Ltd., Himalya International Ltd., and Flex Foods Ltd. are the dominating key players in the Indian mushroom market because of their extensive distribution networks and high-quality product offerings.


Related Blogs











