Drip Irrigation Method: Transforming Indian Agriculture Drop by Drop

Drip irrigation is among the most effective methods to promote water use efficiency in Indian agriculture, which is reeling under extreme water stress. It delivers water, nutrients and chemicals in the right amount at the right place and time with greater efficiency and uniformity. Read on to learn everything about drip irrigation model in India.
Table of Contents
- What is Drip Irrigation?
- What is the Status of Drip Irrigation in India?
- What are the Different Types of Drip Irrigation?
- What are the major components of Drip Irrigation?
- How to Install a Drip Irrigation System?
- How to Maintain a Drip Irrigation System?
- What are the benefits of Drip Irrigation in India?
- What are the Government Initiatives for Drip Irrigation in India?
What is Drip Irrigation?
Drip or trickle irrigation is an efficient irrigation method that results in lower water consumption compared to surface irrigation. A network of pipes, valves and emitters delivers water directly to the roots of the crops. This irrigation technique is highly suitable for most crops, including oilseeds, cash crops, vegetables, and fruits. Additionally, fertigation is used to apply fertilizers through drip irrigation, which carries and distributes water and nutrients.
The root zone receives almost all the water in the drip irrigation system. There is nearly no wetness in the surface area; thus, this method needs 25% less water than surface irrigation. Also, drip irrigation model is suitable for saline soil conditions.
What is the Status of Drip Irrigation in India?
In the 1970s, drip irrigation technologies from developed nations, such as the US and Israel, were introduced in India. 4374.53 thousand hectares were noted to be under drip irrigation in 2019. Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Sikkim and Karnataka are the leading users of drip irrigation.
In 2021-22, the area covered under drip irrigation in Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana (PMKSY) was 3.58 lakh hectares. Also, the largest drip irrigation programme in Asia is the Ramthal (Marol) Micro Irrigation Project located in Karnataka.
What are the Different Types of Drip Irrigation?
The following are the primary types of drip irrigation systems in India:
- Surface Drip Irrigation: This system places emitters and laterals on the surface. It provides water near the root zones of crops and maintains desired soil moisture. There is less soil wetted by surface drip irrigation than by surface irrigation methods.
- Subsurface Drip Irrigation: The installation of emitters and laterals is done below the soil's surface. The most popular systems include the cane wall, T-tape, Typhoon, and Bi-wall systems. They are highly valuable for irrigating row crops.
What are the major components of Drip Irrigation?
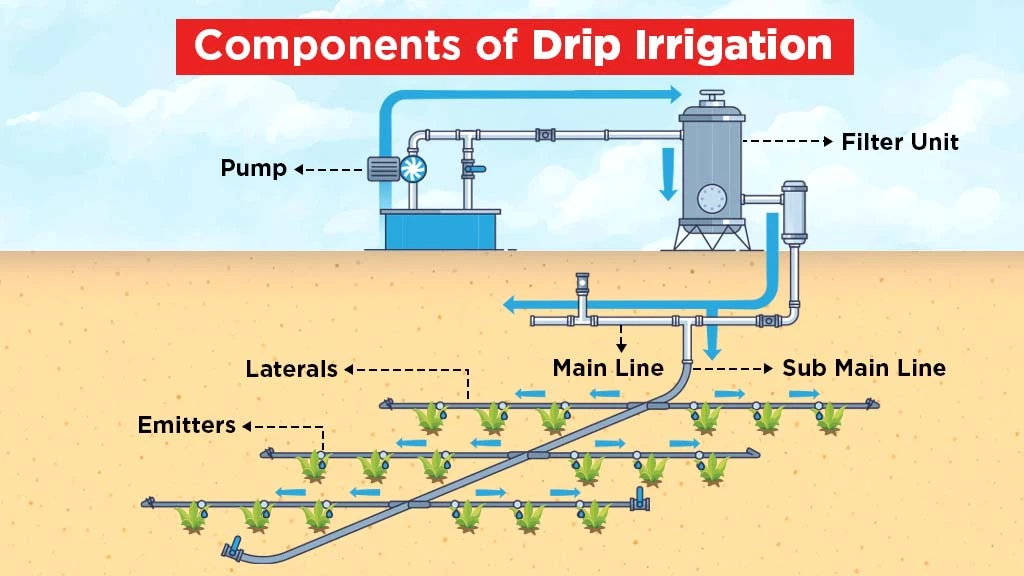
The components of the drip irrigation system have been categorized as:
- Pump: A water pump supplies water at a specific discharge capacity through the system's components, including the fertilizer tank, filtering unit, mainline, and laterals. Different water sources can be used for this system, including canal water, tank/reservoir, lake, river or wells.
- Filter Unit: This component filters out the suspended impurities in water before it reaches pipes or tubes. It does not allow pipes and emitters to clog.
- Mainline: The mainline transports water to the field and distributes it uniformly to the submains. It supplies the total quantity of water needed for the system. Its pipes are generally made of high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or poly vinyl chloride (PVC).
- Sub-mains: Sub-mains can be installed above ground (HDPE) or below ground (HDPE/PVC). Laterals are fed by sub-mains. Generally, the sub mainline has a pressure rating of over 2.5 kg/cm2 and 32-75 mm diameter of pipes.
- Laterals: They are used for uniform water distribution along their length with the help of emitters. Emitters must be mounted or integrated within tubes called laterals. The material used for laterals includes LDPE and LLDPE.
- Emitters: Drip nozzles discharge water from laterals to the soil. Water in the form of trickles is emitted at a slow rate for irrigating crops.
The other components of the drip irrigation model are valves, gauges, water meters, chemical tanks/injectors, etc.
How to Install a Drip Irrigation System?
A drip irrigation system can be installed by following the steps mentioned below:
- Conduct a proper survey of the field to determine the area.
- Obtain all the necessary information, including crop type, row direction, row spacing, and water source details, from the farmer.
- Design the drip irrigation system according to the survey and information collected.
- Make the list of all the components, parts, and quantities needed according to the design.
- Now, proceed to the next step and supply the material.
- Make trench markings and cuts as per the design for laying PVC pipes.
- Now, install the drip irrigation pump to the end cap.
- Perform testing and commissioning of the system.
- You can backfill the trenches if no problems or leakages are found at the time of testing.
- Provide operations and maintenance training for the farmers.
- Finally, hand over the complete drip irrigation system to farmers.
How to Maintain a Drip Irrigation System?
Drip irrigation requires regular maintenance, and you should check the following elements to ensure the efficiency of your drip irrigation system.
- You need to check the Head Control Unit pressure daily.
- You need to clean the filters by cleaning their parts on alternate days or once a week, depending on the quality of the water.
- You should open the flush valves once a week to flush out the main, submain, lateral & dripper lines.
- You should also check the pressure at the end of the lateral monthly.
- After harvesting, you need to perform the acid/chlorine treatment.
What are the benefits of Drip Irrigation in India?
The use of drip irrigation yields various benefits for Indian farmers, including contributions to sustainable agricultural practices. Other key benefits include:
- Water Conservation: Drip irrigation can significantly reduce water usage. There is reduced evaporation and wastage as water is directly delivered to the root zone. Thus, it facilitates the efficient use of limited water resources.
- Higher Crop Yields: The drip irrigation method provides a consistent and controlled water supply, promoting optimal crop growth. Crop health improves due to the precise delivery of water and nutrients. Thus, there is a higher crop yield than with traditional irrigation methods.
- Weed Control: As the irrigation water targets the root zone of plants, the surface is left relatively dry. Thus, the growth of weeds is prevented, and the labour involved in manual weeding is reduced.
- Labour Saving: A well-designed drip system is mainly automated. You just need to start or stop this system. Thus, expenses related to manual labour are considerably reduced.
- Soil Compatibility: Irrigation is also challenging in India because of diverse soil conditions. It isn't easy to irrigate very light soil because of deep water percolation. Also, there are low infiltration rates in heavy soils. Drip irrigation is successful in both soil types.
- Energy Saving: Drip irrigation uses less water because of its high irrigation efficiency. Thus, the time required for supplying irrigation water is reduced. Therefore, the consumption of electricity or any other fuel source required for irrigation is minimized.
What are the Government Initiatives for Drip Irrigation in India?
The Government of India is making considerable efforts to help farmers adopt micro-irrigation. There is a provision for financial assistance/subsidy under the Per Drop More Crop (PDMC) program for installing drip and sprinkler irrigation systems. This subsidy amounts to 55% and 45% of the indicative unit cost for small and marginal farmers, respectively. PDMC is a key component of Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana.
The drip irrigation model is improving water use in agriculture. Its benefits promise a bright future for sustainable agriculture in India. As more farmers utilize government support to adopt this practice, earning a higher income with high-value crops is becoming easier.
Frequently Asked Questions On Drip Irrigation Method: Transforming Indian Agriculture Drop by Drop
1. What is drip irrigation?
Drip irrigation is an efficient micro-irrigation method that slowly drips water to the root zones of plants.
2. What are the uses of drip irrigation?
The uses of drip irrigation include irrigating vineyards and small and large fields while saving water.
3. Who invented drip irrigation?
Simcha Blass, a Polish Israeli engineer, invented the modern drip irrigation system.
4. What are the advantages of drip irrigation?
The advantages of drip irrigation include water conservation, weed control, higher crop yields, and labour and energy savings.
5. How does drip irrigation work?
Drip irrigation makes use of a network of pipes and emitters to supply water at low pressure to the root zones.
6. How does drip irrigation save water?
Drip irrigation saves water due to its precise delivery of water where needed. Additionally, this irrigation method results in less evaporation and runoff.
7. Does drip irrigation make farming more efficient?
Yes, drip irrigation makes farming more efficient. This method optimizes water usage and enhances crop yields.


Related Blogs












