How does a Tractor Engine Work? Different Types of Tractor Engines

Tractors are used for a wide range of applications in agriculture, industrial and construction sectors. They are equipped with powerful engines to derive more power for heavy-duty tasks. In this blog, we will discuss everything about the tractor engine, which is the heart of the tractor. Read on to understand how this engine works and its various types. It will help you make a suitable decision when purchasing a new tractor or servicing and repairing an old one.
Table of Contents
- What is the Role of Tractor Engine?
- What are the Different Parts of Tractor Engine?
- How Does a Tractor Engine Work?
- What are the Different Types of Tractor Engines?
What is the Role of a Tractor Engine?
Engine is the heart of any vehicle, and tractors are no different. A tractor engine generates power, which is transmitted to the PTO and wheels through the transmission system. Thus, it provides power to the tractor to perform all kinds of tasks on and off the road.
Diesel is the most common type of fuel used in tractors. It is because they have a higher compression ratio, which results in better fuel efficiency. Additionally, diesel engines produce higher torque, which is a basic requirement for a tractor. Electric tractors are the latest addition to the Indian market. They lack an internal combustion (IC) engine as they have an electric motor and a battery to generate power for various tasks.
What are the Different Parts of a Tractor Engine?
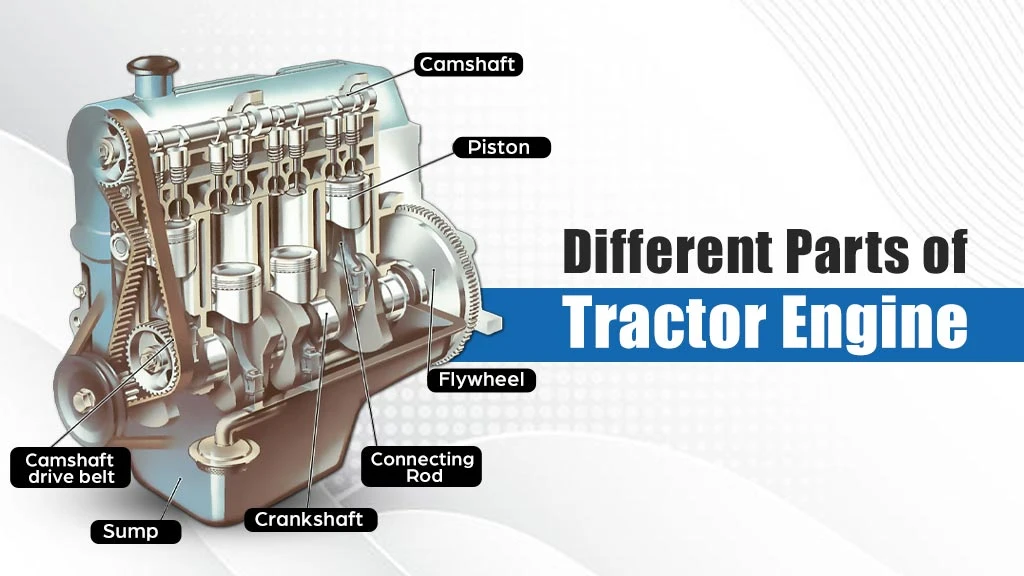
A tractor engine delivers high torque at a low speed. It is an internal combustion engine that generally runs on diesel. So, this engine compresses and burns fuel to produce mechanical motion power. A tractor engine has a complex structure and comprises several parts. The key parts of a tractor engine are listed below:
Cylinder
A cylinder is an essential component of the engine. It is a chamber where fuel combustion occurs to produce power. More cylinders mean more pistons to combust fuel, thus producing more power. The cylinder handles all the pressure and heat generated during fuel combustion. This is why robust materials, such as cast iron, are used to make cylinders. Additionally, it requires a cooling system to manage high temperatures and ensure efficient operation.
Piston
A cylinder houses a piston that undergoes reciprocating motion to compress the fuel-air mixture, causing combustion. A piston produces pressure forces via fuel combustion that are transmitted to rotate the crankshaft using a connecting rod. Its top is called a crown, while the sides are known as a skirt. A piston also must withstand high temperatures and pressure. Thus, it is manufactured from cast iron or aluminium alloy. Piston rings provide the sealing between the piston and cylinder.
Camshaft
This rotating shaft operates the intake and exhaust valves throughout the engine cycle. The camshaft determines the specific duration and precise timing of the valve opening/closing. So, it ensures timely intake of air, combustion of fuel and removal of exhaust gases. The camshaft allows coordinated movement of valves, which is integral to the power output, efficiency and performance of the engine.
Crankshaft
A crankshaft is simply a rotating shaft that changes the reciprocating movement of the piston into rotational motion. The connecting rod transfers the power generated to the crankshaft. The rotational motion of the crankshaft moves the flywheel to move the tractor. The materials used to make a crankshaft are cast iron or forged steel. A crankshaft is an important element of the engine system, as any design error can result in engine failure.
Fuel Injector
A fuel injector injects fuel when the compression stroke ends after atomizing fuel into fine droplets. In an IC engine, the air is forced into the cylinder during the intake stroke. This air is then compressed to extremely high pressure. The fuel is pressurized at high pressure to get atomized. At a specific injection time, a precise amount of fuel is injected into the chamber for optimum combustion. A fuel injector ensures a good quality fuel-air mixture that offers better engine efficiency and lower emissions.
Flywheel
This mechanical device features a heavy disc that can store rotational energy. It provides consistent power to the crankshaft and keeps the engine running smoothly. A flywheel that operates can be considered a temporary reservoir of energy. Its primary purpose is to prevent speed fluctuations in the transmission system. It uses the conserved rotational energy to smoothen the power delivery from the tractor engine. Also, it maintains the angular momentum of the crankshaft during the non-power strokes.
How does a Tractor Engine Work?
A tractor uses an internal combustion engine, which has already been discussed above. The main principle of all IC engines is the same: air mixed with fuel in the correct proportion creates an explosive mixture. This mixture, under extreme pressure, gets ignited and produces power to move the tractor.
The engine draws air into the cylinder. This air is compressed significantly, which increases its temperature to high levels. In the next step, fuel is injected into the cylinder. Fuel combusts immediately due to the high-temperature air. This creates an explosion to generate force to move the piston and drive the crankshaft. Lastly, the crankshaft transmits power to the wheels.
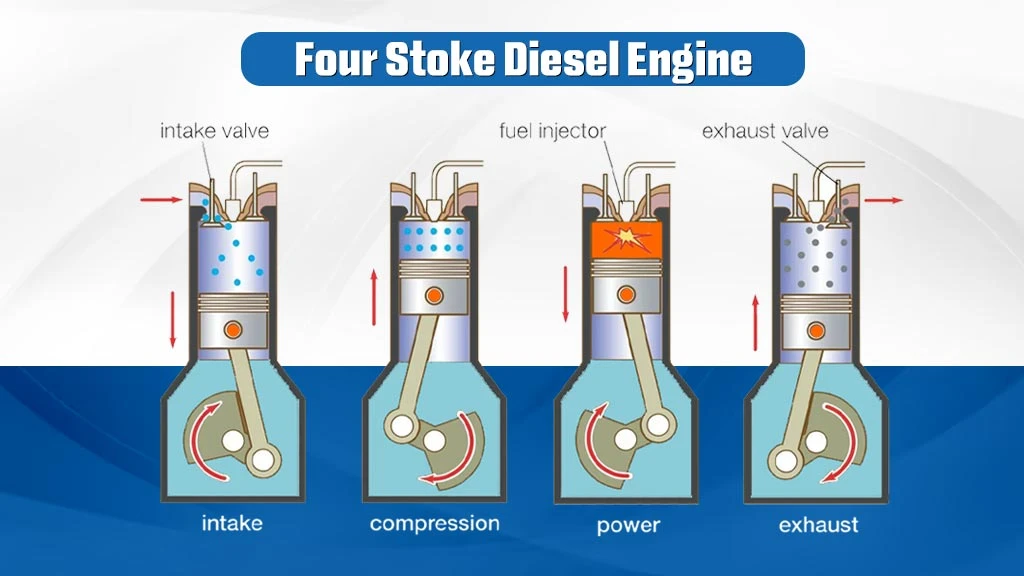
A diesel engine works through the repetition of a cycle of four strokes or stages. In a single cycle, the piston moves from the top to the bottom two times. In other words, the crankshaft of the tractor rotates twice. The firing order of a 4-stroke diesel engine is 1-3-4-2. The operation cycle of the 4-stroke tractor engine involves the following stages:
Intake Stroke
In the intake stroke, the inlet valve opens while its piston moves down the cylinder. So, the cylinder receives air from outside. As the piston moves to the bottom, the air is filled in the cylinder. At last, the inlet valve is closed.
Compression Stroke
First, the inlet valve is closed at this stage. Both inlet and outlet valves are closed in this stroke. As the piston moves up, the air mixture gets compressed in a tight space, which heats it to high temperatures. When the compression stroke ends, fuel is injected into the cylinder. The ignition occurs spontaneously when the fuel comes in contact with pressurized and high-temperature air.
Power Stroke
Both valves remain closed in the power stroke. Due to ignition, extreme heat is generated inside the cylinder. The piston is pushed down due to the high pressure in the cylinder. This downward movement is known as a power stroke. The generated power is transmitted from the piston to the crankshaft with the help of the connecting rod. The crankshaft begins to rotate and transfers power to the wheels.
Exhaust Stroke
The piston travels upward in this stroke. The exhaust gases move out through the exhaust valve. As the burnt gases are eliminated from the tractor engine, the cylinder can receive fresh air, and the cycle continues.
What are the Different Types of Tractor Engines?
The engine is the most crucial component of a tractor as it provides the power needed to perform different farm tasks. Based on how air is drawn into the engine, the tractor engine can be categorized into two types: Naturally Aspirated and Turbocharged. Go through the next section to know which engine type is suitable for your farming needs.
Naturally Aspirated Tractor Engine
In a naturally aspirated (NA) engine, cylinders receive air with the help of atmospheric pressure alone. It means there is no external mechanism or forced induction system to force air into the cylinder. For more power in an NA engine, a larger mix of fuel and air is combusted in the engine. Thus, the manufacturer increases the number of cylinders or their bore to increase the volume of the combustion chamber and derive extra power. This is why naturally aspirated tractor engines are likely to have a larger displacement.
As NA engines have fewer components, they are more reliable, durable and easier to maintain. Their manufacturing cost is also low because of their simple design and fewer parts. This means these tractors are cheaper than tractors with turbochargers. Linear power delivery and instant response make the driving experience more engaging.
However, NA engines offer lower power density. This means that a bigger CC engine is required to produce the same power output as a turbocharged engine. Also, their emission level is higher than that of their turbocharged counterparts, particularly under heavy loads. The popular tractor models in India that come with a naturally aspirated engine are Swaraj 855 FE, Mahindra Yuvo Tech+ 575, Eicher 557, etc.
Turbocharged Tractor Engine
A turbocharged engine is equipped with a turbocharger for force induction of extra compressed air into the engine. This turbocharger has two main components: compressor and turbine wheel. The exhaust gases emitted by the engine enter the inlet port of the turbocharger at high pressure. The turbine wheel spins because of this high-pressure air. This also makes the compressor wheel spin, which causes a vast amount of air to be drawn in and expelled via the exhaust port.
This compressed air travels through an intercooler to be injected into the cylinders. The role of the intercooler is to cool the air, which is heated due to hot exhaust gases. The turbocharged engines are powerful enough to produce the same or even more power output with a smaller capacity than NA engines. Even at lower RPMs, they offer more torque. Thus, the initial acceleration or pickup is excellent. As they use cleaner air, turbocharged engines are more refined and produce less noise.
More components mean higher manufacturing costs. Additionally, these engines are more complex, making their maintenance and repair more challenging and expensive. There is also an issue of turbo lag, which causes a slight delay in the power delivery when the operator accelerates. The popular tractor models that come with turbocharged engine are New Holland 3630 TX Plus Special Edition, John Deere 5310 Gear Pro Trem IV, John Deere 5075 Gear Pro 4WD Trem IV, and many others.
Hope you now understand how a tractor engine works. It will help you maintain and service your tractor. Also, you can now see which engine type is most suitable if you are looking to buy a new tractor. Tractorkarvan has listed a wide range of tractors with all of their key specifications, including the engine and fuel pump type. You can check these details to choose an ideal tractor that fits your farming needs and budget. Remember that a smooth-running engine is crucial for your tractor as it has a huge impact on its performance and fuel efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions On Different Types of Tractor Engines in India
1. What type of engine is used in tractors?
A 4-stroke diesel engine is most commonly used in tractors.
2. How many types of tractor engines are there?
There are two types of tractor engines: naturally aspirated and turbocharged engines.
3. What are the different components of a tractor engine?
A tractor engine consists of different components, including cylinder, piston, camshaft, crankshaft, fuel injector, and flywheel.


Related Blogs












