Hydroponic Farming: Meaning, Benefits, Types and Future in India

Hydroponics is a farming method to grow plants in a nutrient-rich solution. Even though this method does not use soil, it ensures healthy and faster plant growth. The key benefits of hydroponics include efficient use of space and water, higher yield, controlled environment and optimal pest and disease management. Hydroponic farming in India has a huge potential to ensure a prosperous future for the agriculture sector.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Hydroponics
- What is Hydroponic Farming?
- Hydroponic Systems and How They Work?
- What are the Benefits of Hydroponics?
- What are the Different Types of Hydroponics?
- What is the Future of Hydroponics Farming in India?
Introduction to Hydroponics
What is hydroponics? Hydroponics is the cultivation of plants indoors without the use of soil. In hydroponic agriculture, crop roots absorb nutrients from a nutrient-rich solution to ensure healthy and faster plant growth. The hydroponic system allows farmers to grow crops indoors without the use of pesticides.
It is an efficient alternative to traditional farming methods as there is no need for large areas of field and rainfall. Hydroponic farming is a solution to several agricultural issues, such as lack of cultivable land, weed management and wastage of water. The hydroponic method also promotes sustainable agriculture as it does not use chemicals for pest and disease management.
What is Hydroponic Farming?
Hydroponic farming is the practice of cultivating plants in nutrient-rich solutions without soil. Plants are grown in inert growing media. This growing media provides mechanical support to roots of the plants. Examples of hydroponic growing media include coconut fibre, sawdust, rock wool and gravel.
Another key aspect of the hydroponic technique is the direct supply of water, oxygen and nutrient-rich solutions to plant roots. Thus, it ensures high quality, faster growth and higher yields. Several crops and plants are suitable for hydroponic farming. It is highly important to select the correct hydroponic plants as some plants may not grow well in water-based environments.
Examples of popular hydroponic plants include leafy vegetables like Atriplex, Swiss chard, Celery, Microgreens, Pakchoi, Coriander, Spinach and Lettuce. In addition to leafy vegetables, hydroponic vegetables also include Radish, Melons, Cauliflower, Cabbage, Cucumber, Brinjal, Tomato and Capsicum. Hydroponics examples for herbs are Watercress, Parsley, Rosemary and Basil. Thus, the uses of hydroponics include the cultivation of different types of herbs, leafy greens, fruits and vining plants.
Hydroponic Systems and How They Work?
Plants depend on photosynthesis to obtain energy for ideal growth and development. The photosynthesis process relies on solar energy and does not need soil. The role of soil is to supply nutrients and water to plant roots. If the water has a suitable amount of dissolved nutrients, it can be directly provided to the root system of plants. This is the science behind the working of hydroponic systems.
An active hydroponic system supplies nutrients to the roots of plants by moving the solution with the help of a pump. The growing media has a wick/anchor for nutrient delivery in the passive hydroponic system. The inert media in hydroponic cultivation supports plant roots. Soil is replaced by a growing media. It cannot offer any nutrients to plants on its own. Being a porous media, it absorbs nutrients and moisture from the solution, which is then provided to plants.
What are the Benefits of Hydroponics?
- No Soil Needed: Scientific hydroponics is a water-based, soil-less farming method. So, farmers could cultivate crops in areas where there is limited land. Also, it is a key alternative for lands that do not have fertile soils.
- Efficient Space Use: Hydroponic farming is possible in small spaces, including indoor spaces, greenhouses and rooftops. Usually, roots grow deeper and wider to get oxygen and essential nutrients. However, hydroponics provides nutrient-rich solutions to plants directly. Thus, plants grow close to each other, saving plenty of space. Efficient use of space is among the leading advantages of hydroponics.
- Efficient Water Use: As per the research paper in the Indian Farming journal, hydroponic cultivation demands only 10–25% of the total amount of water needed for field-grown plants. Run-off water is recirculated into the hydroponic system. Thus, plants get just the required amount of water.
- High Yield: Plants grow faster in a hydroponic system than in soil. This is because the roots receive the required levels of nutrients and water directly. So, the plant growth is healthy and quicker, which increases the yield.
- Controlled Environment: Like greenhouse farming, hydroponic farming offers complete control over a range of factors affecting plant growth, like light exposure, humidity and temperature. It provides ideal growth conditions for plants, resulting in high-quality produce. Also, farmers can grow plants throughout the year, irrespective of the season.
- Optimal Pest and Disease Management: Traditional agriculture is highly dependent on pesticides and herbicides to protect plants against pests and diseases. Hydroponic farming does not involve the use of such external inputs. It ensures protected cultivation indoors to eliminate the risk of harmful pests and diseases.
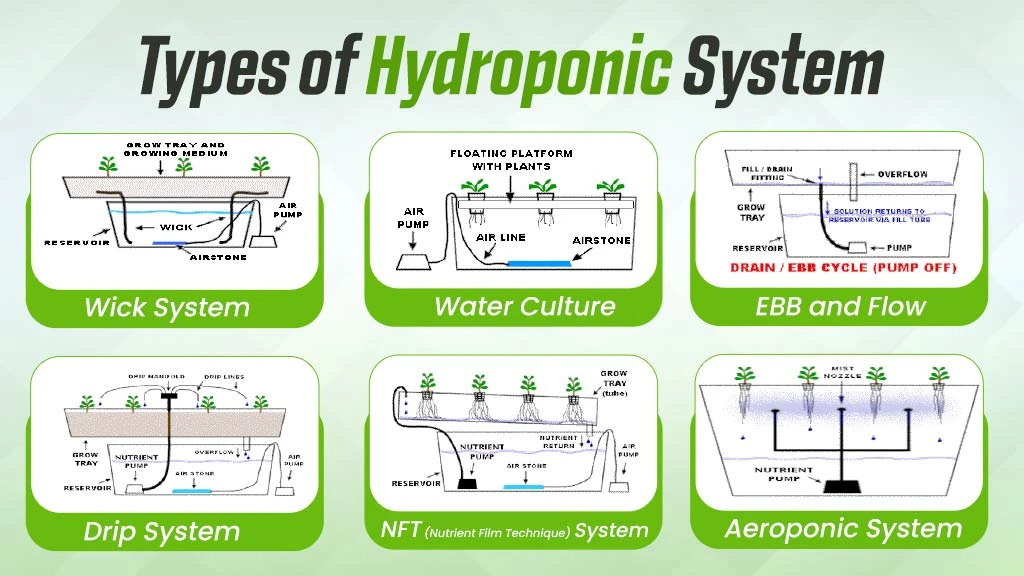
What are the Different Types of Hydroponics?
The different types of hydroponic systems are the Wick system, Water Culture, Ebb and Flow, Drip system, NFT (Nutrient Film Technique) system and Aeroponic system.
What is the Future of Hydroponics Farming in India?
Hydroponic farming is still in the growth stage in India. Most farmers rely on traditional farming or soil-based farming only. The primary market for the hydroponic industry is urban farmers in Tier-1 or metropolitan cities. The scope of this industry is high as India is experiencing rapid population growth. This is why the size of arable land is decreasing quickly. Hydroponics methods have a huge potential to produce suitable amounts of food crops to meet the demands of the rising population.
In addition, hydroponic farming minimizes the use of pesticides and herbicides. This is good for the future of agriculture in India as it will reduce cultivation costs and environmental pollution for farmers. The extreme weather conditions can severely impact agricultural production. For instance, hailstorms and high rainfall damage crops across the country. Hydroponic agriculture is practised in a controlled environment where such challenges are absent.
The future of hydroponics farming in India involves using a systematic plan to adopt and promote hydroponic techniques. There is a need for education and training programs so farmers can clearly understand hydroponic cultivation and its importance.
Research must be undertaken to analyse local conditions like water availability, humidity and temperature. It will help improve nutrient formulations and hydroponic systems as per domestic conditions. If these steps are taken, hydroponic farming will be able to ensure a prosperous future for Indian agriculture.
Frequently Asked Questions On Hydroponic Farming: Meaning, Benefits, Types and Future in India
1. What is hydroponic farming?
Hydroponic farming is a farming method that involves growing plants in a nutrient-rich solution. In this method, soil is not used.
2. Are hydroponic farms profitable?
Even though hydroponic farms demand high setup costs, farmers can easily recover these costs in some years and earn huge profits.
3. Do hydroponic farms use soil?
No, hydroponic farms do not use soil, as plants are grown in a nutrient-rich solution.
4. How much does a hydroponic farm cost?
An hydroponic farm can have a one-time setup cost between ₹18,87,200 and ₹20,00,000. It is applicable for a farm in a 5,000-square-foot area.
5. Is hydroponic farming expensive?
Yes, hydroponic farming is expensive as it uses several modern tools and equipment, like polyhouse shelter, pH meter, TDS meter and RO system.


Related Blogs












