Ploughing in Agriculture: Meaning, Types & Tips

Ploughing, also known as tilling, is the method of turning over and breaking up the soil using a plough or other farm implements to prepare it for plantation. In this blog, we will discuss the different types of ploughs, their working, popular implements, and we will also provide tips for choosing the right plough.
Table of Contents
- What is Ploughing? Meaning and Importance
- What are the Types of Ploughs available in India?
- What are the different Methods of Ploughing?
- What are the Tips for Choosing the Right Plough?
- Which are the Popular Plough Models in India?
- Get Information on Different Types of Plough Online
What is Ploughing? Meaning and Importance
Ploughing is a fundamental farming practice. It is an ancient agricultural practice that breaks and turns the first layer of soil for preparing the land before cultivation. Its purpose is to loosen up the soil to absorb air, bring fresh nutrients to the surface, dump the remains of previous crops, and control weeds.
Ploughing leads to more uniform germination of seeds. It helps in rejuvenating the overused or depleted soil by adding organic matter. A properly ploughed land is less susceptible to waterlogging and drainage issues. It also improves the overall soil structure and soil health.
The invention of the plough revolutionized the entire process of agriculture. The availability of iron played a major role in the evolution of ploughs. Gradually, ploughs started coming with iron ploughshares and wooden carts, which increased their effectiveness. They were used for centuries for Ploughing. Later, at the end of the 18th century, the first all-metal plough was manufactured on an industrial scale. Since then, on the basis of requirements, plough has been evolving. Let’s discuss some of the major types of ploughs in detail.
What are the Types of Ploughs available in India?
Agriculture in India is a mix of traditional and modern farming techniques. Traditionally, wooden ploughs have been used in India for centuries for ploughing the land. The wooden plough, also known as the indigenous plough, is an implement made of wood and iron. It is drawn with the help of bullocks for ploughing the field. Wooden ploughs are still used for Ploughing in India, specifically in underdeveloped areas. However, due to their inefficiency in Ploughing, many modern ploughs have emerged in the agricultural sphere. The modern ploughs are available in different varieties, and they require a tractor to operate. The different types of ploughs available in India are MB plough, Hydraulic Reversbile MB plough, Disc plough, Chisel plough, and Subsoiler. Let’s discuss them one by one:
MB Plough

MB Plough is a primary tillage implement used for cutting, lifting, inverting, and pulverizing the furrow slice. In this type of plough, only one way of soil inversion happens as it throws the furrow slice to one side of the direction of travel. The MB plough is used in the field using the gathering or casting method. They are available in many options, and according to the tractor HP, you can choose a one-bottom, two-bottom, or three-bottom MB plough. The popular MB plough brands in India are Fieldking MB plough, Landforce MB plough, Swan Agro MB plough, and many others.
Hydraulic Reversible MB Plough

The hydraulic reversible MB plough is a more advanced type of MB plough, which is hydraulically operated for ploughing the land. It turns the furrow slice to the left or right side of the direction of travel as needed. These ploughs consist of two sets of opposed bottoms. In this plough, all furrows can be turned towards the same direction of the field by using one bottom for one side of travel and the other bottom for the return trip. The popular hydraulics reversible MB plough brands in India are Shaktiman hydraulic reversible MB plough, Fieldking hydraulic reversible MB plough, Mahindra hydraulic reversible MB plough, and more.
Disc Plough

The disc plough is specially designed for hard and stony soil. It comes with a set of circular blades that cut through the soil and break the clumps easily. It is available in both fixed and reversible types. The common size of the disc is 60 cm in diameter. The popular brands offering disc ploughs in India are Fieldking disc plough, Landforce disc plough, Krishiking disc plough, and many others.
Chisel Plough

Chisel plough is designed especially for deep tillage that causes less disturbance to the top layers. It ploughs the land to a depth of 60 to 70 cm. It has a thin body with a cutting, sharp blade or edge. It does not turn the soil as much as other ploughs, which makes it a suitable option for low till farming. The chisel plough is suitable for ploughing the hardpan soil. The popular chisel plough brands in India are John Deere chisel plough, Vishwakarma chisel plough, and Agrotis chisel plough.
Subsoiler

Subsoiler plough’s shape is similar to a chisel plough, but it has stronger, heavy-duty legs for deep Ploughing. It breaks the hard layers of soil or subsoil without bringing them up to the surface. It ploughs the land up to depths of two feet. The popular subsoiler brands in India are Fieldking subsoiler, Maschio Gaspardo subsoiler, Lancer subsoiler, etc.
What are the different Methods of Ploughing?
Ploughing is done mainly to obtain a deep seedbed which has good water retention and appropriate air. This can be achieved with three main methods of Ploughing, such as gathering, casting, continuous ploughing method, and round and round ploughing method. Let’s discuss them below:
Gathering
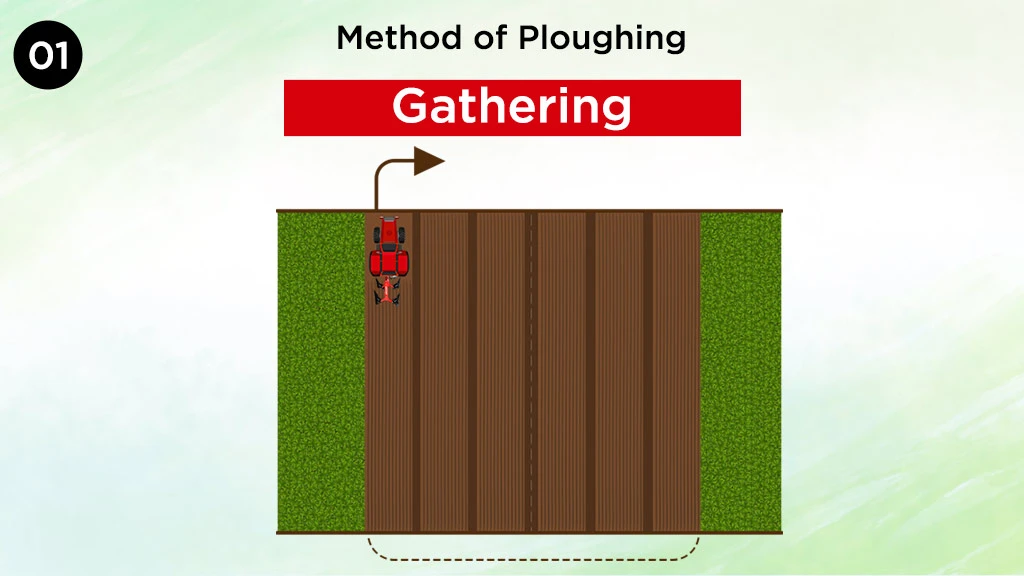
Gathering is a process in which the plough works round a strip of ploughed land.
Casting
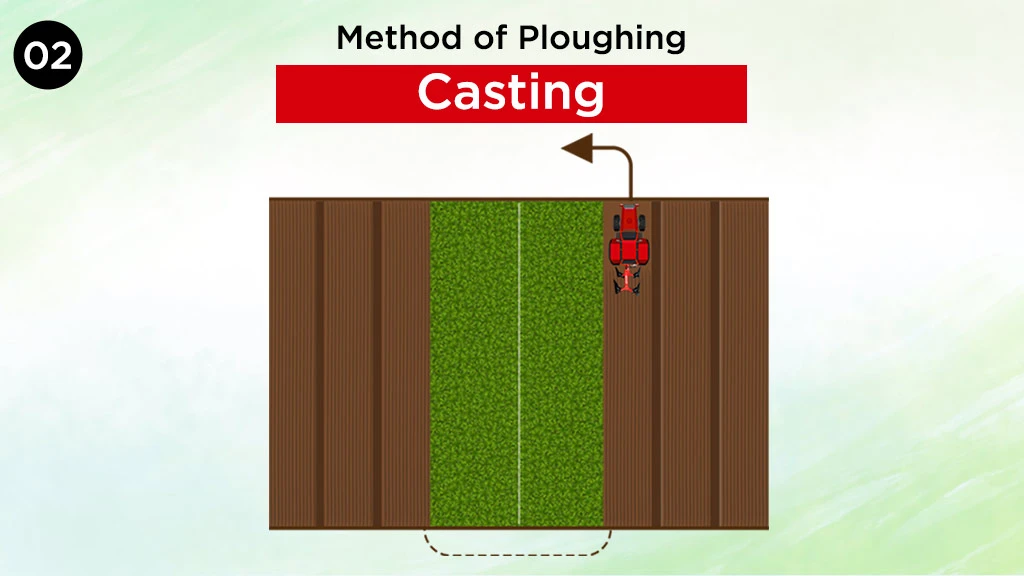
Casting is a process in which the plough works round a strip of unploughed land.
Continuous Ploughing Method
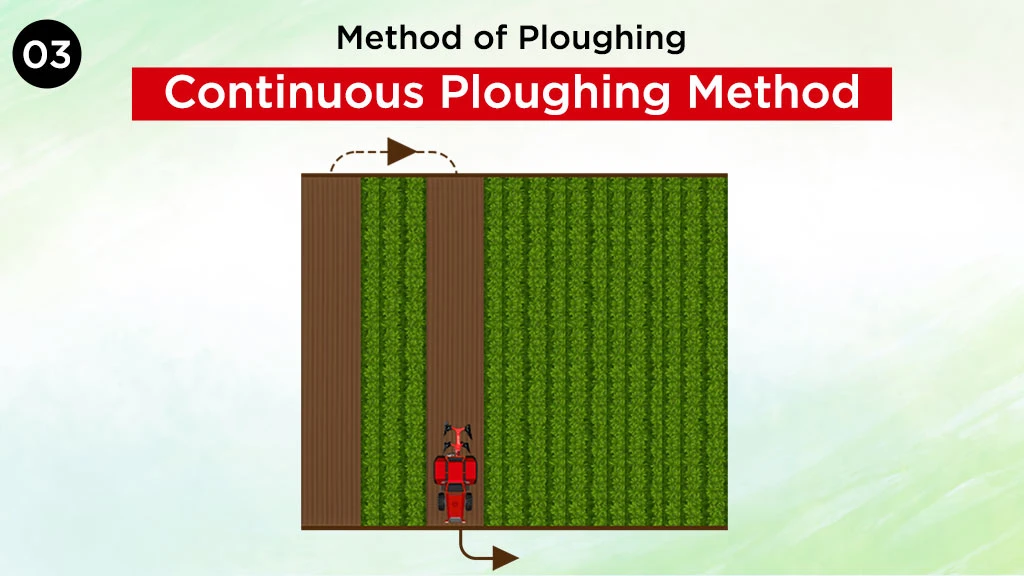
This ploughing method is one of the economical and convenient methods. It is a traditional large-scale farming method that helps in quick seedbed preparation along with weed control. In this process, the tractor and the plough never stay idle beyond three quarter land width along the headland. They also never move in a space narrower than a quarter land width. The Ploughing is done continuously without leaving large sections of furrows unploughed. This method is efficient in enhancing uniformity while Ploughing.
Round and Round Ploughing Method
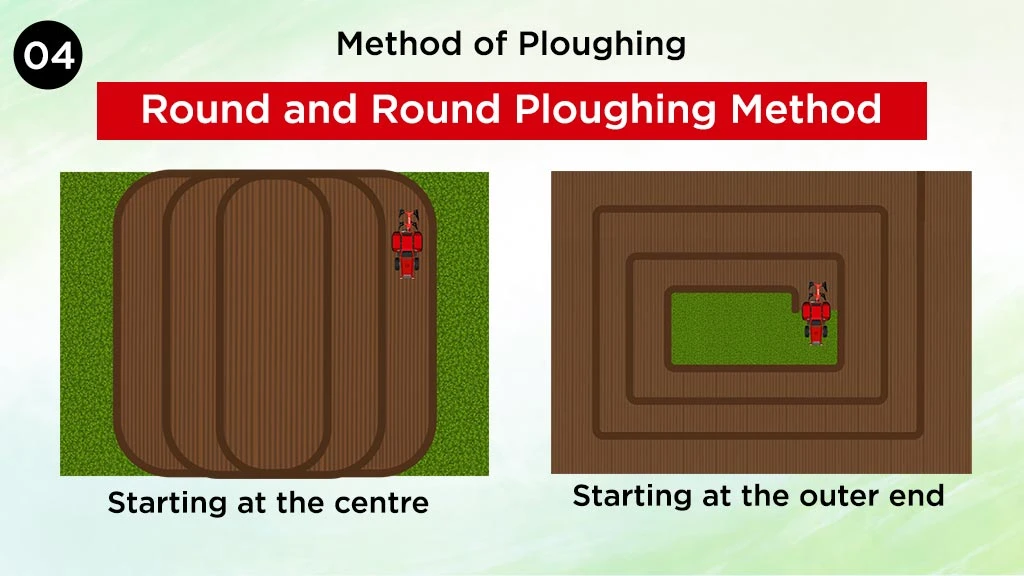
In this method, as the name suggests, the plough moves circularly in the field. The Ploughing starts from one side of the field and gradually it reaches the centre. This method, however, is not a very economical and accurate method, as large diagonals remain unploughed.
What are the Tips for Choosing the Right Plough?
- Analyzing the Soil: The very first step before buying a plough is understanding the soil type of your land. Different soils and crops need different types of ploughs for tilling. For example, in case of loamy soil, the MB plough is a good option, while in case of stony soil, disc plough appears as a better choice. Different crops require different ploughing depths. For example, MB plough or chisel plough is suitable for maize and wheat. Whereas sugarcane might require a subsoiler.
- Tractor Compatibility: The higher the HP of your tractor, the better the ploughing performance. Choose the plough compatible with your engine capacity, HP, and hydraulics. This is because all these factors are responsible for operating the plough smoothly. The 4WD tractors are better at providing stability and traction when it comes to handling implements like a plough. All these factors decide the compatibility of the plough with a tractor.
- Brand Reputation: It is important to choose your plough from a reputable brand that has a good dealer network. It should offer reliable service or spare parts for maintenance and warranty. Good customer support is a benefit as it can help you with any issues you will face with the plough.
- Budget and Cost: Look if there are any subsidies offered by the government on the plough that you want to purchase. If not, then you can always opt for an implement loan at the best interest rates.
- Demo: Make sure you take a demo of the plough before purchasing. It will give you a clear picture regarding its usage, specifically for your farm. You can also check out expert reviews and user reviews to understand whether it fits your requirements or not.
- Expert Advice: If you are unable to judge which plough type would be the right option for your farm, you can reach out to experts for guidance. You can also visit Tractorkarvan for expert advice.
Which are the Popular Plough Models in India?
|
Model Name |
Implement Type |
Tractor Power (HP) |
Price (Rs.) |
|
Disc Plough |
65 – 75 |
75,923* |
|
|
Disc Plough |
50 – 60 |
62,187* |
|
|
MB Plough |
65 – 75 |
47,336* |
|
|
MB Plough |
45 – 60 |
32,497* |
|
|
Hydraulic Reversible MB Plough |
65 – 90 |
3,05,000* |
|
|
Hydraulic Reversible MB Plough |
55 – 70 |
2,16,200* |
|
|
Subsoiler |
55+ |
80,000* |
|
|
Subsoiler |
65+ |
1,60,000* |
Get Information on Different Types of Plough Online
Tractorkarvan is an online platform that provides comprehensive and authentic information on various types of ploughs in India. Here, you can find various models of MB ploughs, disc ploughs, hydraulic reversible MB ploughs, chisel ploughs, and subsoilers, along with their specifications and prices. We have developed a compare implements feature on our portal where you can compare two plough models of similar or different brands. You can explore our plough page, where you can find all the types of plough listed with their complete specifications and prices.
Frequently Asked Questions On Ploughing in Agriculture: Meaning, Types & Tips
1. What is Ploughing?
Ploughing is the method of turning over and breaking up the soil using a plough or other farm implements to prepare it for plantation.
2. What are some types of ploughs used in India?
Some types of ploughs used in India are MB plough, hydraulic reversible plough, disc plough, chisel plough, and subsoiler plough.
3. Why is ploughing important?
Ploughing helps loosen the soil for proper aeration, as well as weed and pest control.
4. What are the different methods of Ploughing?
The different methods of Ploughing include gathering, casting, continuous Ploughing, and round and round Ploughing.


Related Blogs












