Rainwater Harvesting: Recharging Groundwater for a Sustainable Future

The Earth is abundant with water, but ‘water for use’ is very scarce. Rainwater harvesting is the process of collection and storage of rainwater in a tank over the surface or under the surface before it gets wasted as runoff. Various methods of rainwater harvesting are practised in India. In this blog, we will thoroughly understand the rainwater harvesting, such as its importance, benefits, types, government initiatives and some success stories.
Table of Contents
- What is Rainwater Harvesting?
- Why do We Need Rainwater Harvesting?
- What is the Current Scenario of Rainwater Harvesting in India?
- Different Types of Rainwater Harvesting Practiced in India
- What are the Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting?
- What are the Government Initiatives to Promote Rainwater Harvesting?
- Success Stories on Rainwater Harvesting in Indian States
- Conclusion
What is Rainwater Harvesting?
Rainwater harvesting is the method of collecting rainwater and storing it for later use. In this method, rainwater is harvested by constructing a tank over the surface or under the surface before it gets wasted as runoff. Rainwater harvesting is one of the most widely used approaches to ensure sufficient water supply when required for different purposes such as irrigation, domestic use, and others.
Why do We Need Rainwater Harvesting?
- Rainwater harvesting is highly needed to mitigate the water scarcity crisis. It helps overcome the water inadequacy to meet the requirement.
- Rainwater harvesting helps preserving the declining groundwater level and helps enhance water availability in specific regions. The water can later be used for different purposes, promoting sustainable development.
- It also helps increase the water level in the subsoil, which has been declining in urban areas because of the paving of the open areas, so rainwater harvesting is highly needed here.
- It is helpful in improving the water quality through dilution and increasing the productivity in agriculture.
What is the Current Scenario of Rainwater Harvesting in India?
- In Mar 2025, on World Water Day, the Government of India emphasised water conservation and management through community participation and innovative strategies in the sixth edition of Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Catch the Rain – 2025.
- Under the Jal Shakti Abhiyan, between 2022 and 2024, the government has constructed more than 18 lakh water conservation and rainwater harvesting structures with a total expenditure of Rs. 15.20 lakhs.
- Moreover, states like Gujarat, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha and Chhattisgarh have taken up rainwater harvesting programs on a large scale.
Different Types of Rainwater Harvesting Practiced in India
There are different types of rainwater harvesting practiced in India, which are as follows:
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting
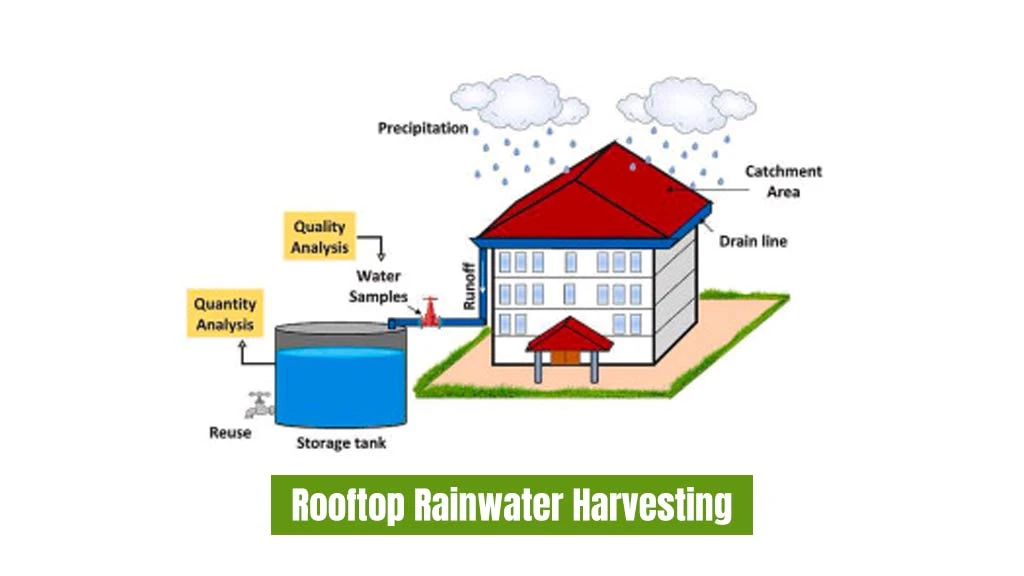
The collecting of water from the rooftop of a house or any infrastructure is known as rooftop rainwater harvesting. The water is collected through pipes or gutter directly connected to the reservoir. This water is then used later for different purposes.
Contour Bunds
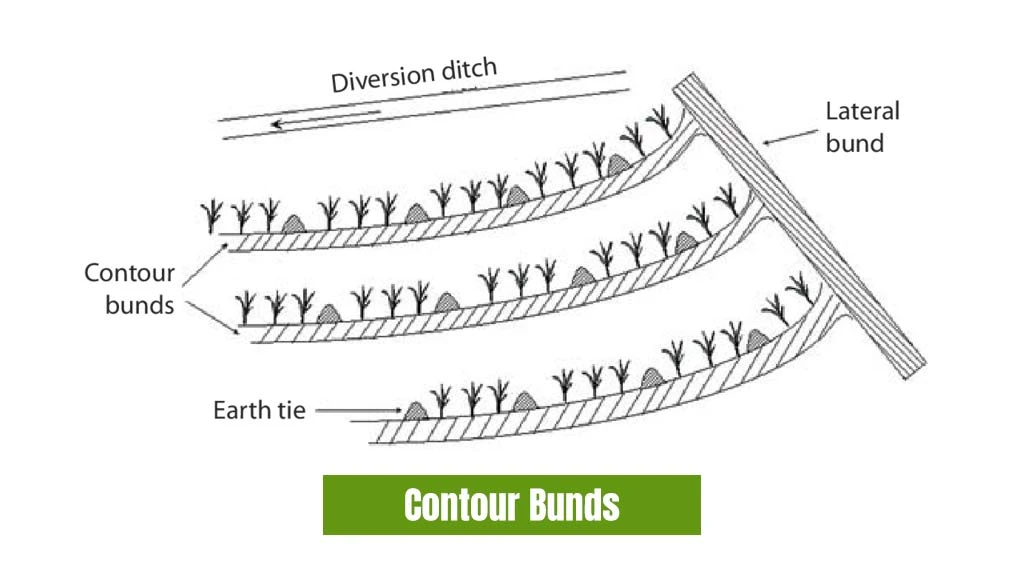
Contour bunds is a technique of rainwater harvesting which involves creating bunds on the sloping land which slow down rainwater runoff and conserves soil moisture. In low rainfall areas, these are well suited as the farmers can easily hold the runoff by creating bunds along the contour with equal elevation. Adequate spacing between buds prevents water from reaching speeds that can erode the land.
Percolation Tanks
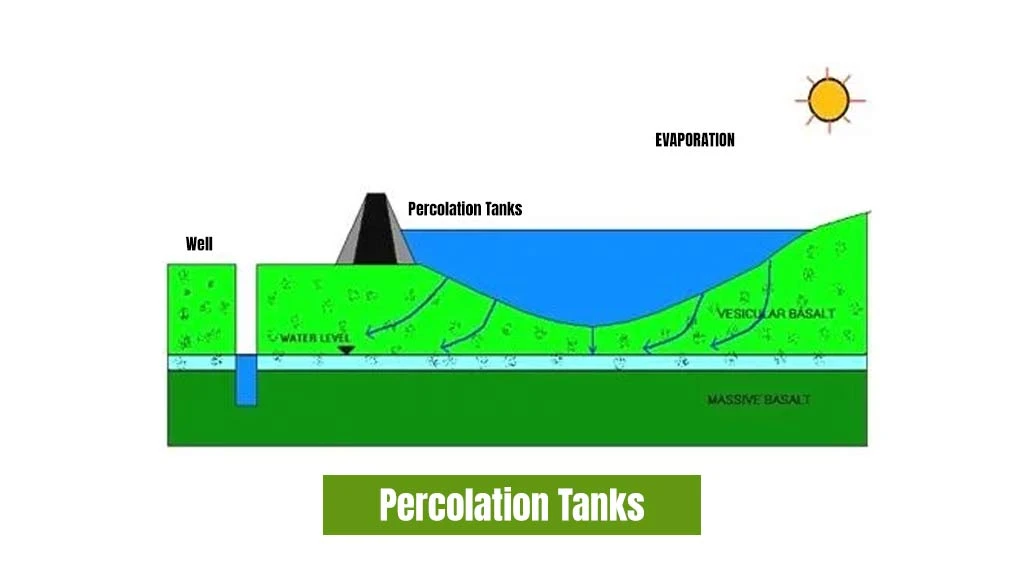
The percolation tanks are the artificially created tanks on the water body to recharge the groundwater. It allows water to infiltrate the ground and replenish the groundwater. These are formed at a significant height from where the water can run down to cultivable lands or wells for most of the benefits of the farmlands.
Check Dams
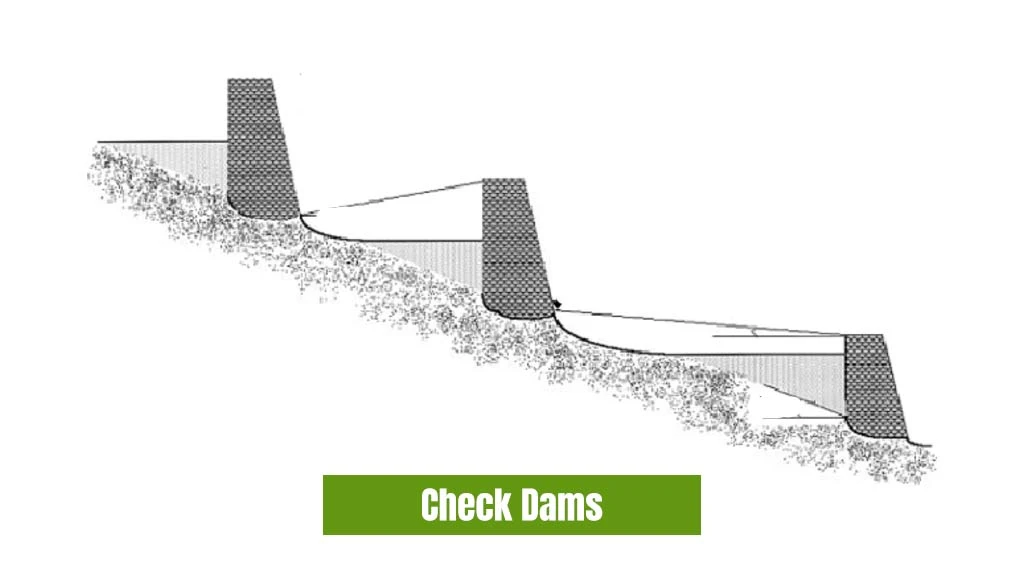
Also known as nala bunds or cement plugs, check dams are constructed on the gentle slope of a small stream. With a height usually less than 2 m, allowing excess water to overflow, it is made to recharge the stored water quickly. Shallow trenches are created to form low-cost check dams. A series of these dams are constructed in the stream or natural drainage channel to gain maximum water recharge using clay-filled cement bags.
Dugwell Recharge
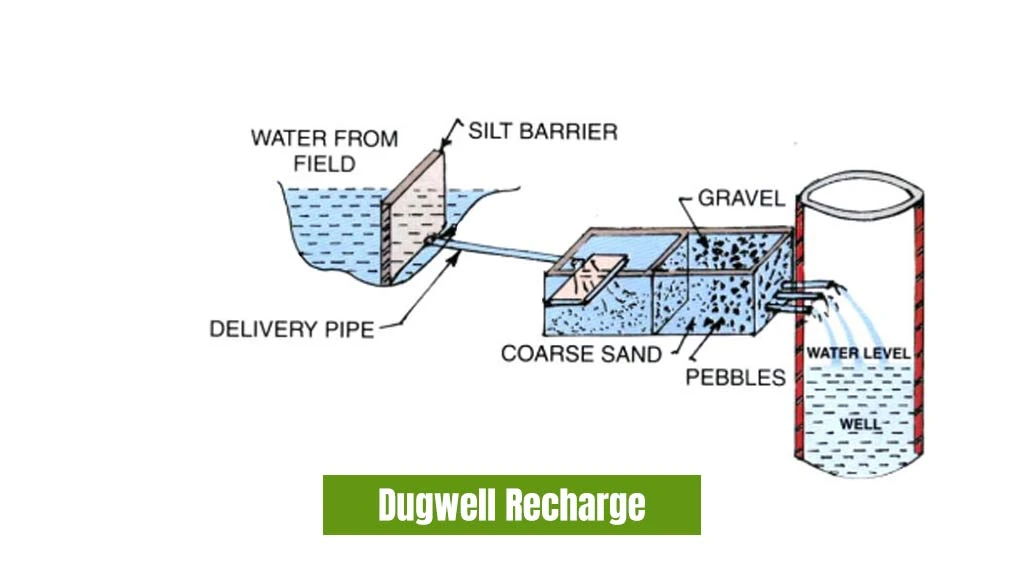
These are the wells that already exist and are used as recharge structures after proper cleaning and desilting. The water is guided to the structure using pipes from the desilting chamber. This structure helps farmers easily gain access to water when required. However, periodic chlorination is required to control bacteriological contaminations.
What are the Benefits of Rainwater Harvesting?

- Water Conservation: The ultimate motto of the rainwater harvesting is to store the water for later use. In this case, rainwater harvesting helps reduce water runoff, as the water is collected in tanks or reservoirs. This ensures water conservation, which can be used for various required activities.
- Increased Water Availability: When the rainwater is harvested and stored, it can be used according to the need without relying on other water sources.
- Reduced Soil Erosion: When the rainwater is harvested, it helps stop soil erosion by reducing water runoff.
- Sustainable Irrigation: Stored water collected from rainwater harvesting can be used for irrigation, thus offering a sustainable irrigation method with a steady supply of water.
- Cost Savings: Rainwater harvesting offers a cost-effective method to access high-quality water, allowing farmers to take advantage of it and use it responsibly for agricultural purposes.
What are the Government Initiatives to Promote Rainwater Harvesting?
Jal Shakti Abhiyan: Launched in 2019 with the tag line “Catch the rain, where it falls, when it falls”, the scheme envisages construction and repair of rainwater harvesting structures through community participation.
AMRUT 2.0: The Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) was launched on 1st October 2021, which aims to focus on universal coverage of functional water tap connections, water source conservation, rejuvenation of water bodies and wells, recycle/reuse of treated used water, and rainwater harvesting.
Atal Bhujal Yojana: This scheme aims for the sustainable management of groundwater with community participation. The programme is in implementation in 80 districts of 7 states, namely, Gujarat, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Karnataka and Rajasthan.
Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchai Yojana (PMKSY): One of the key focuses of the Pradhan Mantri Krishi Sinchayee Yojana is on introducing sustainable water conservation practices with focus on rainwater harvesting.
Mission Amrit Sarovar: Aims to create and rejuvenate at least 75 Amrit Sarovars in every district with the purpose of harvesting rainwater.
National Aquifer Mapping (NAQUIM) Project: The project has mapped about 25 lakh square kilometre of groundwater locations for recharging them.
Success Stories on Rainwater Harvesting in Indian States
Rainwater harvesting is an ultimate solution to combat water scarcity in India. Here are some success stories of rainwater harvesting in Indian states:
Rooftop Rainwater Harvesting, Karnataka
Bangalore city was facing inadequate management of water resources, for which the Government of Karnataka initiated a rooftop rainwater harvesting program. The Bangalore Water Supply and Sewerage Board (BWSSB) encouraged all the residents to install rainwater harvesting systems through subsidies and awareness campaigns. After proper installations, dependency on municipal water supply during dry months was reduced. This improved water quality and reduced chances of flooding in low lying areas.
Farm Pond Development, Maharashtra
In the Vidarbha region, people were facing a problem of droughts and erratic rainfall patterns. To address this problem, farmers constructed small ponds or tanks to capture rainwater runoff from their fields. These ponds helped providing irrigation water during dry spells but also improved soil moisture retention and enhanced overall agricultural productivity.
Traditional Talab Bunding, Rajasthan
To overcome the problem of arid land in Alwar district, the Tarun Bharat Sangh (TBS) organization revived traditional rainwater harvesting structures known as talabs or check dams. These structures stored rainwater during the monsoon season which transformed the arid landscape into fertile ground, enabling communities to grow crops throughout the year. It also helped in the drinking water security because of the replenished groundwater levels.
Conclusion
Water is a precious resource, and its shortage is very common problem in India. With a growing population, urbanisation, over-exploitation of natural resources like groundwater, and climate change have made this precious natural resource scarcer. Rainwater harvesting is a sustainable solution to tackle the water shortage issue in the country and helps to conserve water sustainably to make it available for future human consumption and agricultural use. By adopting the methods like rooftop harvesting and recharging groundwater, and with a collaborative approach to conserve rainwater, we all can make it a real success.
Frequently Asked Questions On Rainwater Harvesting
1. What is rainwater harvesting?
Rainwater harvesting is collecting and storing rainwater in a tank over the surface or under the surface before it is wasted as runoff.
2. What are the advantages of rainwater harvesting?
The advantages of rainwater harvesting are reduced flooding and erosion, less groundwater dependence, use in irrigation, ecological benefits, and lower water bills.
3. How to harvest rainwater?
Rainwater is collected and stored in tanks or reservoirs before it seeps into the ground.
4. How can I use harvested rainwater?
The harvested rainwater can be used in watering gardens, wash applications, laundry, flushing toilets, etc.
5. Why is rainwater harvesting important?
Rainwater harvesting is important as it is highly needed to mitigate the water scarcity crisis.
6. What is rooftop rainwater harvesting?
In this type of rainwater harvesting, the water is collected from the rooftop of a house or any infrastructure. The water is collected through pipes or gutter directly connected to the reservoir.


Related Blogs












