Regenerative Agriculture: A Sustainable Approach to Change India's Farming Culture

Regenerative Agriculture consists of popular farming practices that aim to restore soil health and improve biodiversity. It helps reduce soil degradation through practices like crop rotation, cover cropping and agroforestry, etc. It provides a sustainable pathway to address the challenges of modern agriculture and climate change. In this blog we will get to know regenerative agriculture in detail, along with the popular regenerative agricultural practices in India.
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Regenerative Agriculture?
- What are the Principles of Regenerative Agriculture in India?
- What are the Initiatives and Efforts Taken for Regenerative Agriculture in India?
- Which are the Popular Regenerative Agricultural Practices in India?
Introduction
Agriculture has been the pillar of the Indian economy for decades. It supports over 43% of India's total workforce and contributes around 18% to India's GDP. However, the current agriculture model in India depends too much on using pesticides and chemical fertilizers which causes soil degradation and a decrease in crop yields. To overcome these problems, regenerative agriculture can be used as a promising alternative. This farming method addresses these problems and also improves ecosystem health, providing long-term sustainability. Let's understand the concept of regenerative agriculture in depth.
What is Regenerative Agriculture?
Regenerative Agriculture is a farming practice that focuses on restoring soil health and improving biodiversity. The regenerative agriculture practice focuses primarily on reducing soil disturbance, promoting crop rotation, cover cropping, agroforestry, etc. These methods enhance soil fertility, improve the durability of the land against extreme weather conditions and decrease its dependency on external factors.
What are the Principles of Regenerative Agriculture in India?
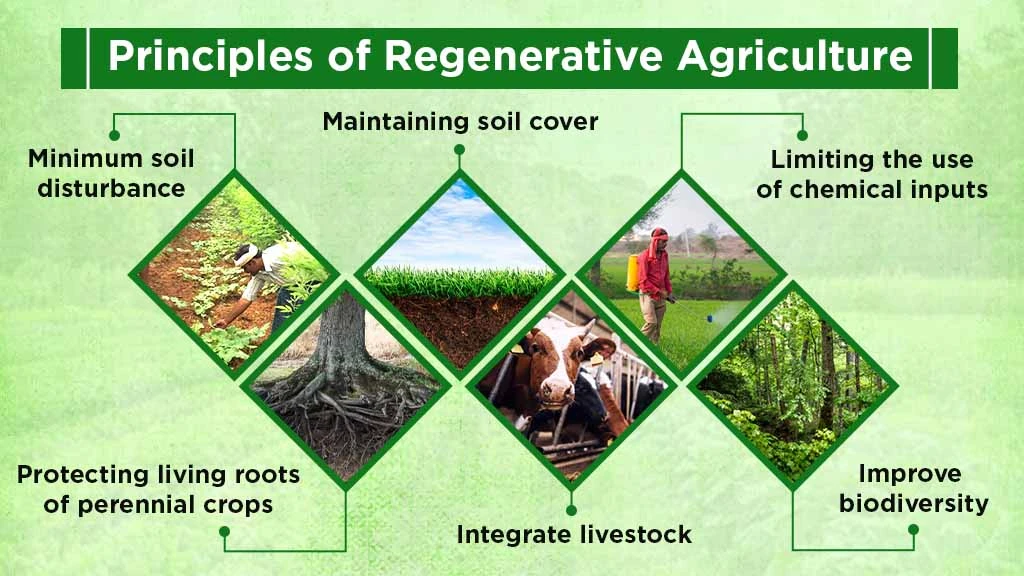
Following are the principles of regenerative agriculture in India:
- Minimum soil disturbance
- Maintaining soil cover
- Limiting the use of chemical inputs
- Improve biodiversity
- Protecting living roots of perennial crops
- Integrate livestock
What are the Initiatives and Efforts Taken for Regenerative Agriculture in India?
In recent times, the government of India has started supporting regenerative agriculture as a response to environmental and economic challenges caused by conventional farming. In 2015, the Indian government launched the Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY), promoting organic farming methods that support regenerative principles. Some Indian states like Andhra Pradesh have developed Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF), which has received international recognization.
In the private sector, organizations like the Indian Council of Agricultural Research are making farmers aware and training them about regenerative agriculture. One more example is Diageo; under its regenerative agriculture program, it has partnered with local groups to provide smallholder farmers with the best knowledge, practices, and tools to transform agricultural methods.
Many Indian startups are leveraging technology to simplify regenerative farming. For example, soil sensors and AI-drive tools are now being used in agriculture and are helping farmers optimize their resources and monitor soil health.
Which are the Popular Regenerative Agricultural Practices in India?
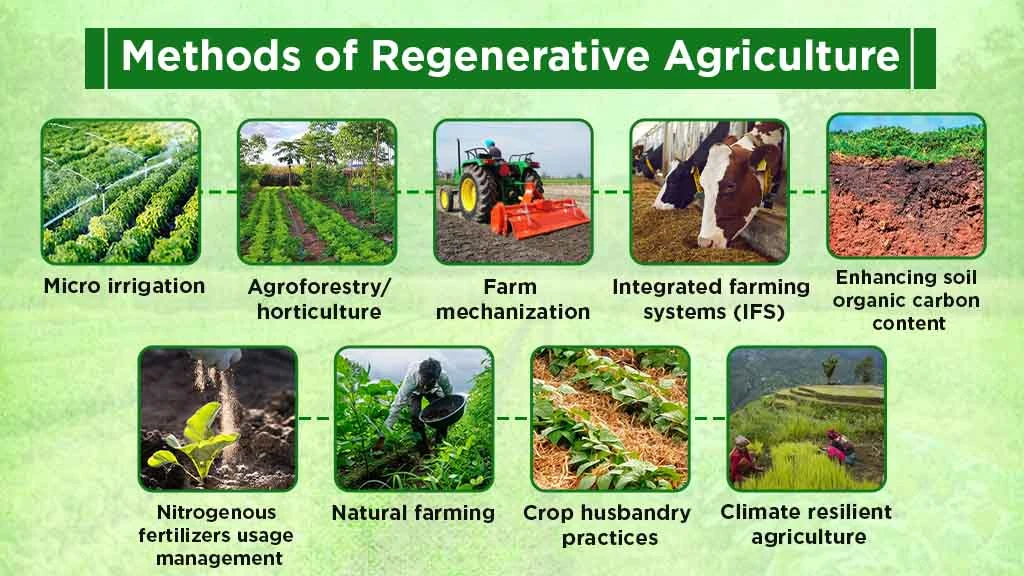
There is a wide range of regenerative agriculture practices performed in India. Some of the popular ones are discussed below:
Micro Irrigation
The National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA) helps farmers through micro-irrigation. It is a key part of the Per Drop More Crop (PDMC) initiative provided under the Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY). Micro-irrigation techniques also include drip irrigation and sprinkler irrigation. These techniques are applied to improve water efficiency and optimize water resources available at the farm level. Farmers in India can minimize water wastage and enhance crop yield by adopting micro irrigation techniques. It plays a vital role in adaptation to climate change by reducing drought impact and extreme weather events on agriculture. As per the report of ICAR, the reduction in emission achieved from the total area of 13.78 million hectares under micro irrigation is around 10.90 millions of CO2e.
Agroforestry/Horticulture
Agroforestry with perennial tree systems of fruit and plantation crops, a sustainable system of land use whose aim is to increase income, conserve resources and provide supplementary livelihood opportunities. In the climate change context, agroforestry provides benefits such as enhanced soil moisture retention, microclimate moderation, and carbon sequestration. Both agroforestry and dryland agriculture based agricultures methods in rainfed ecosystems help in the greening of parched lands which covers 50% of net cultivated land and offer ecological security and livelihood during the long run. These methods help to mitigate the effects of erratic rainfall patterns, enhance resilience in agricultural systems, and contribute to greenhouse gas emissions reduction.
Farm Mechanization
It refers to the use of agricultural machinery and equipment to streamline and automate agricultural operations. Farm mechanization optimizes the use of inputs such as water, fuel, and fertilizers, resulting in a minimized carbon footprint and enhanced environmental sustainability. Additionally, using advanced technologies and precision farming methods ensures better resource management, minimized waste and maximized productivity.
Integrated Farming Systems (IFS)
Integrated Farming System is a combination of crops, fishery, livestock, and other farming activities such as agroforestry, horticulture, and apiculture. It aims to improve livelihood opportunities, reduce risks related to crop failure, and ensure food security. This system promotes farming practices such as intercropping, rotational cropping, multi-cropping, mixed farming and other allied practices. IFS provides many benefits from the climate change perspective, which include increased resilience to extreme weather conditions like floods and droughts. These diversified agricultural systems help farmers sustain their livelihoods, maximize their returns, and mitigate the effects of climate change.
Enhancing Soil Organic Carbon Content
Enhancing soil organic content (SOC) of agricultural soil is beneficial to offset the GHG emissions through sequestration. One popular way of increasing SOC in soil is by adding organic matter regularly as FYM or compost. You can also increase SOC through green manuring, crop residue management, and adopting cereal-legume rotations. These ingredients enhance the percentage of nitrogen and carbon in the soil, which can promote the growth of microorganisms and enhance soil structure.
Nitrogenous Fertilizers Usage Management
Nitrogen management practices influence emissions of nitrous oxide in agriculture. These practices include the type of fertilizer, timing, placement, fertilizer application rate, and coordinating application timing with irrigation and rainfall events. The nitrogen use efficiency can be improved using deep-embedded super granular urea, leaf colour chart, cyanobacteria, and intercropping with legumes.
Natural Farming
Natural farming is a self-sustaining indigenous farming practice that aims to reduce water usage, enhance soil health, and improve SOC in agricultural soil. It ensures enhanced agrobiodiversity, soil biology, and more sensible water usage with smaller nitrogen and carbon footprints. This farming method does not use any synthetic chemicals; thus, it eliminates hazards and health risks. The food developed through natural farming has higher nutrition density and, therefore, provides better health benefits. Farmers practicing natural farming are encouraged to follow 365 days cover-cropping, multi-cropping, etc., while reducing soil disturbance. The Indian government is also launching the National Mission on Natural Farming to promote natural farming among farmers.
Crop Husbandry Practices
It involves green manuring, cover cropping and mulching.
- Green manuring is the process of growing specific plant species that are later mixed into the soil to improve soil fertility and structure. It enhances soil moisture retention capacity, sequesters CO2, minimizes erosion, and promotes the nutrient cycle. It is a natural and cost-effective method to enhance soil health, limit the reliance on synthetic inputs, and enhance crop yield.
- Cover cropping is a farming practice in which crops are planted to cover the soil rather than harvesting. It secures the soil from eroding and sustains the SOC level of the soil. It is a popular practice that minimizes the tillage of the land. Some examples of cover crops are barley, wheat, legumes, lentils, and maize.
- Mulching is another farming practice in which organic materials cover the soil, such as leaves, straw, crop residue, peat, etc., which conserves soil moisture, enhances soil productivity, and minimizes runoff.
Climate Resilient Agriculture
Through the NICRA program, ICAR demonstrated location-specific Climate Resilient Technologies (CRTs) to deal with climate variability in vulnerable districts to develop awareness and build farmers' capacity. It covers crop production, natural resource management, livestock and fisheries. Some innovative institutional interventions developed in NICRA villages are farm implements, water sharing groups, seed and fodder production systems development of commodity groups, community nurseries and initiating collective marketing by tapping value chains, etc. This regenerative agricultural practice focuses on natural resource management and its sustainable application. Therefore, it provides a huge scope for VCM.


Related Blogs












