Growing Crops through Vertical Farming: A Modern Agriculture Practice

Vertical farming involves growing crops in vertical layers in a closed and controlled environment to save water and land space and achieve all-year-round production of more fruits and vegetables. Let's explore this modern agricultural approach in detail, including its major crops, methods, advantages, and challenges faced by farmers in India. So, what are we waiting for? Let's dive into the blog.
Table of Contents
- What is Vertical Farming?
- Types of Vertical Farming
- What are the Advantages of Vertical Farming?
- What are the Top Vertical Farming Companies in India
- Vertical Farming Model: How Vertical Farming Works?
- Which are the Popular Methods of Vertical Farming?
- What are the Challenges in Adopting Vertical Farming?
- What is the Future of Vertical Farming in India?
What is Vertical Farming?
Vertical farming is a modern agricultural method in which crops are grown in vertically stacked layers, often within controlled environments such as greenhouses, or specially designed buildings. This type of farming is highly useful in urban or land-scarce areas, as it enables higher crop yield per area compared to traditional farming. This farming method uses indoor spaces and is practised in an environment where temperature, light, humidity and water supply are tightly regulated, ensuring year-round production regardless of the external environment.
The vertical farming market is still in its early stages, but is gaining popularity in urban areas a a solution for food security and sustainable agriculture. In 2022, the vertical farming market was valued at USD 42.2 million and is projected to increase to USD 187.9 million by 2030, growing at a CAGR of 20.5% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2031.
Types of Vertical Farming
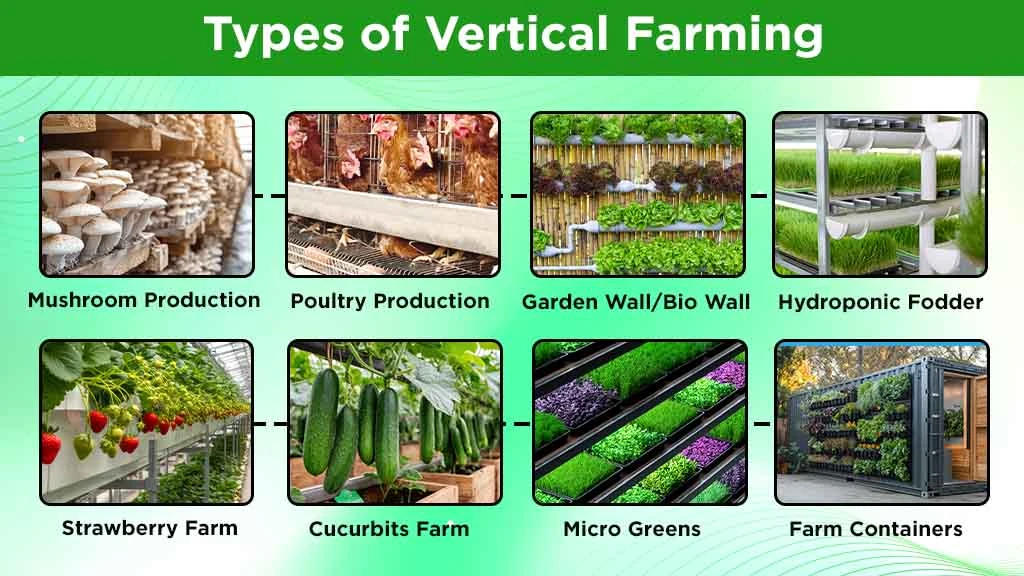
Vertical farming can be used to grow a variety of crops, mushrooms, or even utilised in poultry or fishfarming. The type depends on several factors: the available space, crop demand and budget. Below are some examples of vertical farming ventures in India include:
Mushroom Production
Mushroom production is one of the most successful forms of vertical farming. It is mainly due to the fact that mushrooms do not require sunlight to grow and thrive on organic waste. They can grow in dark, humid and temperature-controlled environments, perfectly suited for vertical indoor setups. In vertical farming, mushrooms are cultivated in stacked layers, trays or shelves. Mushroom production is an apt example of successful, economical and sustainable vertical farming.
Poultry Production (Broiler and Eggs)
Poultry birds, particularly layers (egg producers) and broilers (meat birds), are grown in either multi-story structures with floors or battery cages. Poultry farming is done in Battery cages which are capable of accommodating a larger number of birds, making the business more profitable.
Garden Wall/Bio Wall
Vertical gardening is an innovative way to transform vertical spaces, such as walls, into lush, green oases by growing plants, herbs, fruit, or vegetables upward. These gardens are an excellent fit for urban settings, where space is constrained, as they can be set up both indoors and outdoors.
Hydroponic Fodder
Hydroponic fodder systems offer a viable way to improve livestock farming's sustainability by offering a regulated environment for the productive cultivation of nutrient-rich sprouting grains. This creative approach maximizes resource use and minimizes waste to meet issues like water scarcity and land scarcity.
Strawberry Vertical Farming
Traditional strawberry farming is often limited by various factors, including soil health, space availability, and climate variations. Vertical farming addresses these challenges by providing a controlled and regulated environment where high quality Strawberries can be cultivated. Due to the independence from external factors, vertical farms also helps achieve more harvest cycles per year, leading to significantly higher yields.
Cucurbits Trained Vertically
The cucurbitaceous crops are traditionally cultivated horizontally on the ground. Due to this, cucurbits farming can occupy a lot of space and are also prone to a number of insect pests and diseases. Vertically farming of cucurbits plants helps tackle these challenges to produce healthy yield. In vertical gardens, vines are trained to climb a trellis or garden netting, which helps accommodate larger plant population leading to multiple productivity under open field condition. The important cucurbit crops for vertical farming include cucumber, bottle gourd, sponge gourd, ridge gourd, snake gourd, and bitter gourd.
Micro Greens
Microgreens are young, edible seedlings of vegetables and herbs, harvested 1-3 weeks after germination, at the cotyledon or first true leaf stage. In vertical farming, Micro greens are one of the most ideal crops due to their small size, short growth cycles and minimal space requirements. Microgreens typically grow on vertical farms for 2 to 3 weeks. During a single cultivation cycle, it is possible to sow multiple seed species simultaneously. They are grown in hydroponic vertical farming systems and are cultivated on mats made of natural fibers such as hemp, flax, or coconut.
Farm Containers
Container farming is a method of growing crops in a controlled environment within shipping containers. The containers are climate-controlled and use indoor growing lights to replicate sunlight, creating optimal growing conditions year-round. These ‘farms’ can be placed virtually anywhere, from urban rooftops to rural areas, providing fresh produce locally and reducing transportation costs and carbon footprints.
What are the Advantages of Vertical Farming?
The key benefits of vertical farming are efficient land use, year-round crop production, water conservation, and fewer chemicals.
- Vertical farming technology grows more crops with relatively less land space. The per square meter crop yield is considerably increased in vertically stacked structures.
- Aeroponics and hydroponics are popular vertical farming systems that use less water than traditional methods. Due to the closed-loop systems, vertical farming recirculates water, minimizing water wastage.
- The need for chemicals like herbicides and pesticides is reduced in indoor environments. The risk of diseases and pests is minimized in a controlled environment.
- Vertical farming offers climate resilience, due to which year-round production is possible. The closed-loop system protects plants from seasonal changes and extreme weather conditions.
What are the Top Vertical Farming Companies in India?
Vertical agriculture is becoming popular in India as a sustainable way to grow food in cities. For example, vertical farming in Tamil Nadu is practised by the Kryzen Biotech hydroponic farm in Salem.
Here are some of the top vertical farming companies in India:
- Future Farms
- UrbanKissan
- Agricool India
- Letcetra Agritech
- Triton Foodworks
Vertical Farming Model: How Vertical Farming Works?
There are four major areas to understand how vertical farming works. These are:
- Physical Structure: Vertical farming aims to grow more crops per square meter. For this purpose, a tower-like structure is needed to cultivate crops in stacked layers.
- Lighting: The vertical farming model prioritizes artificial lighting to provide ample light to crops. LED lights are used to enhance lighting efficiency while being cost-effective. A balance between artificial lighting and sunlight can be achieved to ensure a suitable light level in the building.
- Growing Medium: Typically, vertical farming does not use soil. It focuses on soilless technologies like hydroponics, aquaponics and aeroponics.
- Sustainability: Vertical farming adopts sustainable practices to produce eco-friendly food. Thus, it uses less water and no chemicals and reuses resources.
Which are the Popular Methods of Vertical Farming?
The most popular techniques of vertical farming are aeroponics, aquaponics and hydroponics. Let's understand each of these methods in detail below.
Aeroponics
No liquid or solid medium is used in aeroponics. Air is used to produce crops. The roots of plants are suspended in a mist or air environment rich in nutrients. The crops receive key nutrients through a nutrient-rich mist. This vertical farming technology increases productivity and allows for faster growth rates. Also, there is efficient use of water.
Hydroponics
Hydroponics uses nutrient-rich water solutions to provide vital minerals to the roots directly. You can precisely deliver nutrients without wastage of water. Thus, the growth is faster, and crop yield is higher.
Aquaponics
Aquaponics mixes aquaculture and hydroponics to cultivate plants and fish together. This system involves farming soilless plants and rearing fish in tanks. It creates a balanced system in which plants purify the water used for fish, and the same water acts as a natural fertilizer for plants because of their nutrient-rich characteristics.
What are the Challenges in Adopting Vertical Farming?
The major challenges in adopting vertical farming in India include high costs and high energy consumption. The other challenges include:
- Cost-intensive cultivation.
- Considering vertical farming as supplementary farming.
- Partial or no-plant nature interaction.
- Developing ideal varieties or hybrids of ideal crops.
- Lack of infrastructure and expertise.
- Producing unpleasant odour/smell over time (cannot be referred to as total environment-friendly technology).
What is the Future of Vertical Farming in India?
Vertical farming in the coming years will be more high-tech so that more food is produced while being more sustainable. It will address the present challenges of vertical farming, like high costs and energy consumption. Even though it has many limitations, vertical farming has the potential to produce ten times more per unit area compared to traditional agriculture. It also has the scope of integrating into the present and futuristic lifestyle of food production and consumption. It is a sustainable farming method with many benefits, such as less requirement for land, fertilizers, water, pesticides and other inputs. Vertical farming will definitely become a key part of modern agriculture. Future vertical farming is going to be more scalable, cost-effective and accessible.
Frequently Asked Questions On Growing Crops through Vertical Farming: A Modern Agriculture Practice
1. What is vertical farming?
Vertical farming is an innovative approach to growing crops vertically in reduced space and a controlled environment.
2. Is vertical farming eco-friendly?
Yes, vertical farming is eco-friendly as it uses fewer resources like water, fertilizers and land.
3. How does vertical farming work?
Vertical farming uses vertically stacked structures to grow crops using methods like aeroponics, aquaponics and hydroponics.
4. What are the advantages of vertical farming?
The advantages of vertical farming are year-round crop production, fewer chemicals, efficient land use and water conservation.
5. What can be grown in a vertical farm?
A vertical farm can grow a variety of crops, including strawberries, vine crops, leafy greens, herbs, microgreens, and medicinal plants.
6. How to start a vertical farming business?
You can start a vertical farming business by selecting a suitable building and functional farming system in a good location.


Related Blogs












