Sericulture Process in India: Importance and Types

Table of Contents
- Types of Silk in India - Geographical Indications of Indian Silk
- Major Silk Producing States in India
An Introduction to Sericulture
The word Sericulture is derived from the Greek word ‘Sericos’ meaning ‘silk’ and ‘culture’ meaning ‘rearing’. It is the process of rearing silkworms to get the final production of silk, which is the yarn obtained out of cocoons spun by certain species of insects.
Importance of Silk Production in India
India is the second largest producer of silk in the world. As per IBEF, among the four varieties of silk produced in 2022-23, Mulberry accounted for 75.59%, Tasar 3.60%, Eri 20.09% and Muga 0.71% of the total raw silk production of 36,582 Metric Tonnes in 2023. Silk production is an important practice in India due to several reasons:
- Sericulture is an Agro-based rural industry with large labour involvement and high-income generation potential.
- It is one of the most beneficial types of industry for marginal and small-scale farmers.
- Women from rural areas also participates in sericulture which leads to increase in women empowerment.
- Mulberry requires less water, so it is beneficial for the farmers to grow this type of silk in areas under low rainfall areas.
- It gives self-employment opportunities to the youth in rural areas.
- Silkworm and mulberry have many pharmaceutical properties.
- Many by-products are obtained from sericulture activities.
Types of Silkworms
- Mulberry Silk
- Eri Silk
- Tasar Silk
- Muga Silk
India is the only country to produce all four types of silk. The following are the four types of silkworms. Let’s understand each in detail.

Mulberry Silk
Mulberry silk comes from the silkworm, Bombyx mori L. Silkworms feed on mulberry leaves. Hence the rearing of silkworms involves cultivation of mulberry trees, which provide a regular supply of leaves. These silkworms are completely domesticated and reared indoors. Mulberry silk has a pure white colour.
Eri Silk
Eri silk is the product of the domesticated silkworm, Philosamia ricini that feeds mainly on castor leaves. It is also known as Endi or Errandi, Eri is a multivoltine silk spun from open-ended cocoons, unlike other varieties of silk. A white or bright red silk is produced from this type.
Tasar Silk
Tasar silk is generated by the silkworm, Antheraea mylitta which thrive on the food plants like Asan and Arjun. The rearing is conducted in nature openly. It is less lustrous than mulberry silk but has its own feel and appeal. It is usually produced in copper colour.
Muga Silk
Muga silk is obtained from semi-domesticated multivoltine silkworm, Antheraea assamensis. These silkworms feed on the aromatic leaves of Som and Soalu plants and are reared on trees like that of Tasar. It produces a bright golden yellow colour.
Sericulture Process
- Moriculture
- Rearing of Silkworm
- Silk Reeling
Sericulture process consists of three steps. Let’s discuss each in detail.
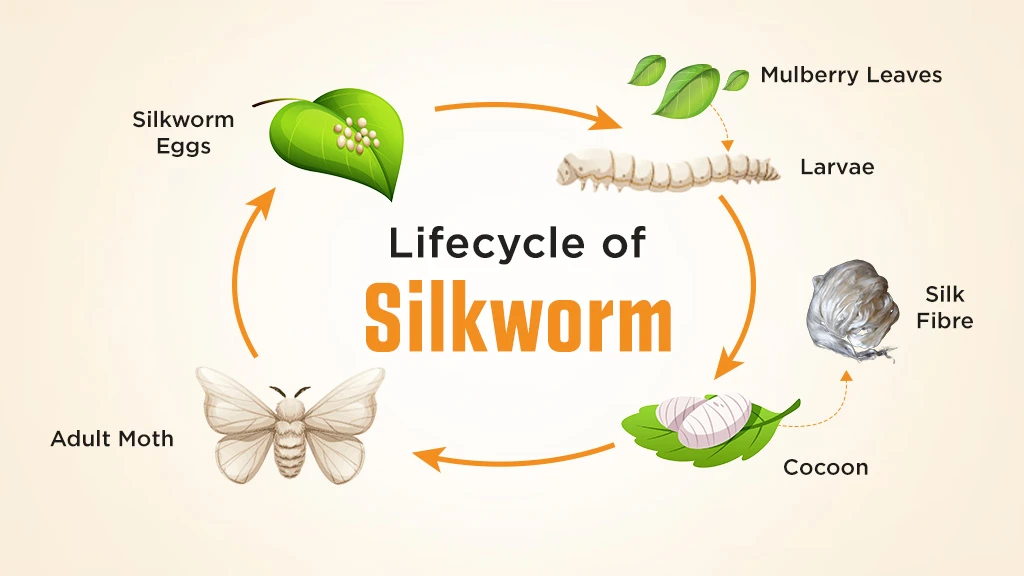
Moriculture
Moriculture is the cultivation of mulberry plants. The leaves are used as food for silkworms. They can be grown by three different methods:
- Seed cultivation
- Root-grafting
- Stem grafting
There are basically three species cultivated in India namely Morus Alba, Morus Indica and Morus Nigra. But the most preferred one is Morus Alba because it grows well in loamy soil. Neutral pH is suitable for the healthier mulberry plants. The mulberry leaves can be taken up as a feed for silkworm after harvesting for the next cocoon stage.
Rearing of Silkworm
The rearing of silkworms begins with the laying of eggs by female silk moths. One single female silk moth produces 300-500 eggs. A 2% formalin solution is needed to disinfect the eggs. The eggs need suitable temperature so that young organism called caterpillar or silkworm break the shell and come out of the egg. The best time is when mulberry leaves bear fresh leaves. Silkworms feed on the mulberry leaves and grow. Along with mulberry leaves the silkworms are kept in clean bamboo trays for about 25-30 days. After some days, the cocoon is formed with a silk fibre and the caterpillar develops into a silk moth.
Silk Reeling
Silk reeling is the next step after silk rearing. The cocoons are kept under the hot sun or exposed to steam, to separate the silk fibres. This process is called stifling. Silk reeling is the process of separating silk threads from the cocoon of the silkworm. The harvesting of silk from these cocoons is the final stage of sericulture. The filament of threads is removed by using different machines to form reels. This spinning of silk fibres produces silk yarn or silk thread. By weaving the yarn, the silk fabric is produced. This is the final silk produced for the garment construction.
Types of Silk in India - Geographical Indications of Indian Silk
- Baluchari Saree - West Bengal
- Salem Silk - Tamil Nadu
- Arani Silk - Tamil Nadu
- Molakalmuru Sarees - Karnataka
- Ilkal Sarees - Karnataka
- Muga Silk - Assam
- Orissa Ikat - Odisha
- Kancheepuram Silk - Tamil Nadu
- Mysore Silk - Karnataka
- Chanderi Fabric - Madhya Pradesh
Major Silk Producing States in India
- Karnataka
- Andhra Pradesh
- Assam
- Tamil Nadu
- West Bengal
According to Central Silk Board of India, these are the top 5 silk producing states in India. Let’s discuss each in detail.
- Karnataka - Karnataka holds the title of being India’s largest silk producer, with its prominent variety of Mysore Silk. During 2022-23, Karnataka produced a total of 11823 metric tonnes silk in the country. Mulberry, Muga, Eri and Tasar silk are found here. Clothing items like sarees, dress materials, and scarves are famous in the state.
- Andhra Pradesh – Being the 2nd holder in the list, Andhra Pradesh has a total production of 9312 metric tonnes in the year 2022-23. The important silk production centres of Andhra Pradesh are in Dharmavaram, Pochampalli, Venkatagiri, and Narayanpet. Mulberry is the attraction, but other types of silk is also found here.
- Assam – Assam ranks 3rd in the silk production in India with 5721 metric tonnes production in 2022-23. It is the largest producer of Muga Silk in the world. Though Assam produces all the 4 varieties of silk, yet major emphases have been given in production of Muga and Eri Silk which are popularly a Vanya Silk. Assam Contributes 95% and 65% of country’s total Muga and Eri production respectively.
- Tamil Nadu - Tamil Nadu stands at fourth position in India, practicing Mulberry sericulture. Rearing of Eri silkworms for production of spun silk has also picked up recently. It has a total production of 2589 metric tonnes.
- West Bengal – West Bengal holds the 5th position with 1966 metric tonnes silk production in the country. The state is famous for producing Mulberry, Muga, Eri and Tasar Silk. The famous items are sarees, shawls and scarves.
Frequently Asked Questions On Sericulture Process in India: Importance and Types
1. What is sericulture?
Sericulture is the process of rearing silkworms to get the final commercial silk production which is the yarn obtained out of cocoons spun by certain species of insects.
2. How is sericulture done?
Moriculture, Rearing of Silkworm and Silk Reeling are the important steps involved in sericulture.
3. What is the importance of sericulture?
Sericulture is an Agro-based rural industry with large labour involvement and high-income generation potential.
4. Is sericulture profitable?
Yes, sericulture is profitable as silk is in high demand in India which helps in gaining maximum profit in less investment.
5. How much money we need to start a Sericulture business in India?
There is a need of approximately 14000 INR per acre (excluding the land and rearing places cost) to start the sericulture business in India.
6. What are the benefits of Sericulture?
Sericulture is a tool for economic reconstruction of rural areas as it provides many employment opportunities to the people.


Related Blogs












