Organic Farming in India - Meaning, Types and Benefits

As we are becoming aware of more environmentally friendly approaches to agriculture, the need for sustainable agricultural farming methods is becoming very important for our country. One such method to facilitate sustainable agriculture is organic farming. Organic farming aims to develop a balanced relationship between nature and agriculture, while also promoting a better future for people and the environment. In today’s blog, we will explore the meaning, types and benefits of organic farming in India. So, stay tuned till the end of this blog.
Table of Contents
- What is Organic Farming?
- What is the Need for Organic Farming in India?
- What is the Present Scenario of Organic Farming in India?
- What are the Different Types of Organic Farming?
- What are the Organic Farming Methods?
- What are the Benefits and disadvantages of Organic Farming?
- What are the Government Efforts to Promote Organic Farming?
- Is Organic Farming Profitable in India?
What is Organic Farming?
Organic Farming is also known as eco-farming, green farming, biological farming or ecological farming. It is an eco-friendly method of agriculture practice that focuses on growing crops using natural fertilisers such as organic manure, compost, and bio-fertilisers. Bio-pesticides are used to protect the crops. It avoids the use of synthetic fertilisers and chemical pesticides entirely, instead relying on using natural resources such as crop residue, animal waste, legumes and other eco-friendly pest management practices. This helps keep the soil healthy and fertile. Techniques like crop rotation, polyculture and natural pest control are used to ensure a sustainable form of farming.
What is the Need for Organic Farming in India?
The need for organic farming in India is to:
- Protect and preserve the environment.
- Prevent soil degradation and maintain soil health.
- Preserve helpful organisms.
- Reduce the emergence of new pests and diseases.
- Protect human health by producing quality food for human consumption.
Today, organic farming is a solution to growing crops without harming the environment or human health.
What is the Present Scenario of Organic Farming in India?
As per the APEDA report for FY24, India has around 7.3 million hectares of land dedicated to organic cultivation, which includes 4.5 hectares of certified organic land, and 2.8 million hectares is being used for wild harvests. India ranks second globally in the number of organic producers, making up 30% of the world's total organic farmers. Madhya Pradesh is the leading state in organic certification, followed by Maharashtra, Rajasthan, Gujrat, Odisha, Sikkim, Uttar Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Kerala, Karnataka, and Andhra Pradesh.
What are the Different Types of Organic Farming?
Two types of organic agriculture are widely practiced across the country: pure organic farming and integrated organic farming.
Pure Organic Farming
Pure organic farming completely avoids using inorganic farming inputs like chemical fertilizers and pesticides. Instead, it focuses on growing crops using organic manure and bio-pesticides.
Integrated Organic Farming
It is a cyclical, zero-waste process in which waste produced through one method is used as a fertiliser or raw material in another. This approach combines integrated nutrient management and integrated pest control to maintain a balance between ecology and economic demand.
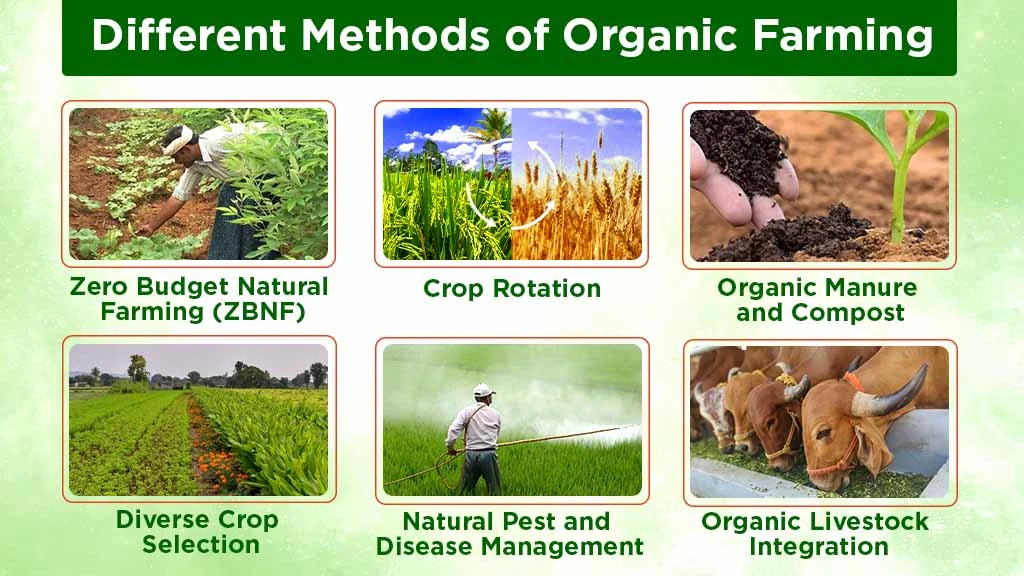
What are Organic Farming Methods?
Various organic farming methods are crop rotation, organic manures and compost use, diverse crop selection, natural pest and disease management, and organic livestock integration. Let us see these methods briefly in the sections below.
Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF)
Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF) is a farming approach where crops are raised without using synthetic fertilizers, pesticides and other external chemicals or materials. ZBNF refers to the concept of eliminating the cost of production by using only natural resources. ZBNF methods require 50-60 percent less water and electricity (than non-ZBNF) for all the selected crops. ZBNF considerably lowers methane emissions by various aeration. This method of farming aims to improve soil fertility, reduce production costs, and enhance income by focusing on sustainable agriculture practices.
Crop Rotation
The crop rotation method involves growing different crops on the same piece of land according to different seasons. It helps maintain soil health and fertility, prevents the growth of insects and pests, and effectively controls weeds.
Organic Manures and Compost
This method uses organic manures and compost to add essential nutrients to the soil. Organic manures are natural fertilizers derived from plant and animal residues. On the other hand, compost is a recycled organic fertilizer created by mixing plant leftovers, kitchen waste, and other organic matter.
Diverse Crop Selection
One effective method of organic farming is crop diversity, also known as 'Polyculture'. This method involves cultivating different crops concurrently to reduce the crops' vulnerability to specific pests and diseases and support the ecosystem.
Natural Pest and Disease Management
It involves using natural methods and beneficial insects to control pests and diseases. It obliterates the need for chemical pesticides.
Organic Livestock Integration
It involves integrating livestock farming with crop farming. In recent years, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has been promoting this agricultural production system in regions with potential for organic farming.
What are the benefits and disadvantages of Organic Farming?
|
Benefits of Organic Farming |
Disadvantages of Organic Farming |
|
Organic farming promotes a healthy environment by avoiding harmful chemicals. |
Organic farming can incur high cost and low yield during initial years. |
|
Organic produce is free from any toxic chemicals, making it healthier for consumers. |
There is a shortage of knowledge about organic production, processing, transportation and certification, especially in more rural areas of the country. |
|
This type of farming helps improves soil fertility and soil health. |
Obtaining organic farming certification can be time consuming and expensive |
|
Over time, organic farming reduces production costs and increases farmers income. |
Marketing and distribution of organic produce is costly compared to conventional farming. |
What are the Government Efforts to Promote Organic Farming?
Since 2015-16, the Indian government has been undertaking initiatives to encourage organic farming across the country. It has launched a number of schemes and strategies to achieve this goal.
Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY)
The Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY) was introduced in 2015 as a comprehensive initiative to promote organic farming in India by using a cluster model. It aims to encourage farmers to pursue organic farming. This includes the following:
- The aim of this initiative is to mobilise farmers to join 50-member clusters covering 20 or 50 hectares of land.
- The clusters will support farmers in obtaining Participatory Guarantee System (PGS) certification for organic crops, allowing them to market their products locally.
- Farmers within a cluster receive financial assistance of INR 50,000 per hectare, up to a maximum of one hectare.
- Educate farmers on the benefits of organic inputs like Panchagavya and Jeevamruth and encourage their adoption.
Since 2015-16, an area of 11.85 lakh ha has been brought under organic farming through the PKVY initiative, and the government plans to dedicate another 6.00 lakh ha to organic farming through PKVY between 2022-23 and 2025-26.
Mission Organic Value Chain Development for the North-Eastern Region (MOVCDNER)
In 2015, the Central Government announced the Mission Organic Value Chain Development for the Northeastern Region (MOVCDNER). It aims to promote certified organic production in the value chain by:
- Its goal is to develop certified organic produce in the value chain through:
- Empowering 30,000 – 50,000 farmers in the region through the creation of 100 FPOs.
- Bringing 50,000 hectares under organic farming in the North-Eastern region of India.
Under this scheme:
- A grant of Rs. 46,500/ha for three years is provided for the establishment of an FPO, as well as assistance to farmers in the form of organic inputs, quality seeds/planting material, training, handholding, and certification.
- Out of this, farmers receive support at Rs. 32,500/ha for three years for off-farm/on-farm organic inputs under the scheme, which includes Rs. 15,000 as DBT and Rs. 17,500 for planting materials.
National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP)
In 2001, the Ministry of Commerce launched the National Programme for Organic Production (NPOP). It specifies the processes for obtaining certification for organic products.
- The main goals are to create a platform for evaluating the certification of organic produce.
- Recognise certification programs for bodies seeking accreditation.
- Ensure organic items are certified to acceptable criteria.
- Encourage organic farming and processing across the country.
Is Organic Farming Profitable in India?
Organic farming is a profitable, environmentally friendly, and productive alternative to conventional farming. According to research, organic farming not only increases yields for major crops such as cereals, oilseeds, and vegetables, but it also offers greater net returns in 63% of the crops evaluated despite its relatively higher production expenses. This method of farming uses eco-friendly, low-cost bio-fertilisers, minimising reliance on costly chemical inputs and improving soil health. The system prioritises biodiversity conservation and natural habitat restoration, which benefits the surrounding ecosystem.
Organic farming in India requires a higher initial investment in land, infrastructure, and equipment. However, the net returns reported in most situations is higher, hence making organic farming a commercially feasible approach that also provides long-term ecological and health benefits. Organic farming is a progressive agricultural technique that combines profitability, environmental responsibility, and long-term resource sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions On Organic Farming in India - Meaning, Types and Benefits
1. What is organic farming?
Organic farming involves the use of organic manure and bio-compost for growing crops. It avoids the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
2. What are the advantages of organic farming?
Organic farming promotes biodiversity, produces quality crops for human consumption, maintains soil fertility and health, and is environmentally friendly.
3. What are some examples of organic farming in India?
Zero Budget Natural Farming (ZBNF), Crop Rotation, Organic Manures and Compost are some of the examples of organic farming.
4. Is organic farming profitable in India?
Yes, Organic farming is profitable, sustainable, and productive compared to inorganic farming due to higher yield, low cultivation costs, and an environmentally friendly approach to agriculture.


Related Blogs















