Cash Crops - Meaning, Types and Importance

Cash crops are mainly grown for commercial purposes to be sold in India and foreign for profits. Cash crops are an essential source of income for Indian farmers, which has led to strengthening the India economy. In this blog, you will learn about different types of cash crops, advantages, importance and risks. Let's read the entire blog to gain a deeper understanding.
Table of Contents
- What are Cash Crops
- Why are Farmers shifting to Cash Crops?
- Major Types of Cash Crops in India
- What are the Benefits of Cash Crops in India?
- Risk Factors of Growing Cash Crops
- Conclusion
What are Cash Crops?
Cash crops, also known as commercial crops, are grown primarily for sale in the market. Also, the purpose of growing these crops is to sell them in the market rather than consuming them personally. Unlike food crops that farmers grow to feed their families, cash crops are generally grown to generate income. A wide variety of commercial crops are grown in India due to the country's diverse climatic conditions and fertile soils. There are multiple varieties of cash crops grown in India including cotton, jute, sugarcane, tobacco, spices, tea, coffee etc, and widely sold in national and international markets.
Why are Farmers Shifting to Cash Crops?
There’s no doubt that farmers are shifting towards growing cash crops. As per the Department of Agriculture and Farmers’ Welfare’s 3rd Advance Estimates, the area under commercial or cash crops like sugarcane, cotton, jute, and mesta has increased from 18.21 million hectares to 18.94 million hectares in 2023-24. The following are some significant factors contributing to India's growing trend towards cash crop cultivation:
- According to the NITI Aayog report, India's food grain production will readily satisfy future demand, with a projected supply of 386.25 million tonnes by 2032–2033, against a demand of 337.01 million tonnes. Farmers have the opportunity to diversify into higher-paying cash crops without worrying about food security due to this stability.
- The National Food Security Mission (NFSM) actively supports food grain production through technology dissemination, high-yield seeds, improved farming tools, and training. This ensures food grains remain secure, freeing farmers to explore commercial crops.
In order to ensure farmers, receive at least 50% more than their production costs, the government guarantees minimum support prices for 22 required crops, including cash crops. Farmers' chances of making more money are increased when they invest in cash crops because of this safety net. This is the main reason why farmers are shifting to cultivate cash crops.
Major Types of Cash Crops in India
The three major types of cash crops grown in India are Cotton, Jute, and Sugarcane. Let's discuss each of them one by one.
Cotton

Cotton is one of the oldest cash crops in India, and our country is the second-largest producer of cotton globally after China. Around 25 per cent of the world's total cotton is produced in India. Our country's estimated earnings from cotton exports were approximately 14887 crores in the financial year 2021-22. Thus, it highly contributes to the country's economy. Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Telangana are the major cotton-producing states in India, accountable for more than 65 per cent of the total cotton production in the country. Generally, three types of cotton are cultivated in India, which include long-staple, medium-staple, and short-staple cotton.
Jute

Jute is another important cash crop widely known as "golden fibre." India is first among the largest jute-producing countries in the world. Jute cultivation requires a temperature between 26 degrees and 35 degrees Celsius. It is a kharif crop, and it requires heavy rainfall for growth. The major Jute producing states in India are West Bengal, Assam, and Bihar, which contribute to more than 95 per cent of the total production in the country. It is widely used as a raw material in textile industries for the manufacturing of fabrics, carpets, household items, etc.
Sugarcane
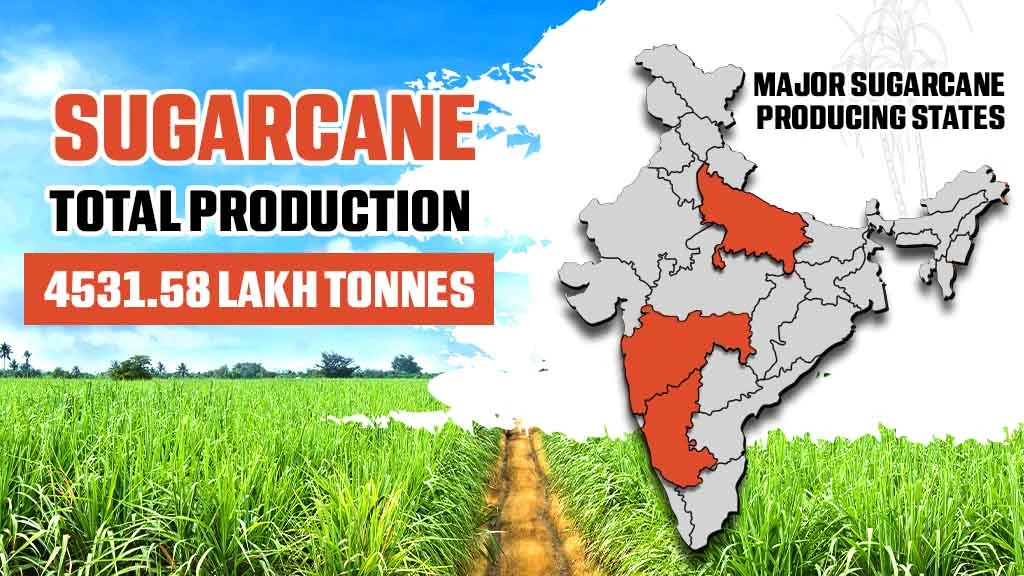
Sugarcane is widely used as a raw material in the sugar industry. Sugarcane cultivation is done on a large scale, and nearly 5.15 million hectares of area are under sugarcane cultivation in the country. India ranks second among the largest sugarcane producers in the world, with an estimated production of 431.81 million tons in the financial year 2021-22. Uttar Pradesh is the leading sugarcane-producing state in India, followed by Maharashtra and Karnataka. Sugarcane is primarily used for the production of sugar and ethanol in India.
What are the Benefits of Cash Crops in India?
- Cash crops provide good income and profits to farmers, helping them raise their living standards.
- Cash crops create substantial revenue through exports, contributing to the country's economy.
- The cash crops produced in India are in high demand in the international market, resulting in better trade relationships and economic diplomacy worldwide.
- Cash crop farming helps farmers diversify their income source and reduces dependency on traditional crop farming.
- Cash crop farming also leads to industrial growth as various industries, such as textiles, sugar, etc., rely on cash crops for raw materials.
Risk Factors of Growing Cash Crops
The cultivation of cash crops involves certain risks. The risk factor could be related to crop type, climate, location, agriculture practices, and market conditions. Some major risk factors are discussed below:
Market Price Fluctuation: Cash crops are price sensitive, and their prices depend on various factors, such as weather conditions, global supply and demand, etc. Thus, there is a risk factor of not getting the expected return if the price drops significantly.
Input Cost Instability: It includes various expenses such as seeds, pesticides, fertilizers, machinery, etc. Thus, any fluctuation in the input cost can affect the farmer's profitability.
Decreased Soil Quality: Without proper soil management, repeated cultivation of a single crop can result in soil degradation and loss of soil fertility. Thus, maintaining soil nutrients and investing in soil conservation is important to overcome this issue.
Dependency on Single Crop: Cultivation of a single cash crop at a large scale can enhance the risk of crop failure. Thus, using crop rotation techniques or diversifying crops can help to sort out this issue.
Limited Market Access: Farmers may face this risk because of the lack of infrastructure for transportation and storage of cash crops in rural areas. Thus, it can restrict their capability of selling their crops at a profitable rate.
Risk of Government Policies & Regulations: Many government policies, trade agreements, and regulations are made for the cash crop market, and changes regarding tariffs, subsidies, or environmental regulations in these policies can impact farmers' profitability.
Conclusion
Cash crop farming in India is an integral part of farmers livelihood and economy, acting as a catalyst for rural development, export earnings and agricultural growth. However, maintaining a balance between the cultivation of cash crops and sustainable agriculture is important to support environmental sustainability.
Frequently Asked Questions On Cash Crops in India
1. What are cash crops?
Cash crops are crops grown for the purpose of selling in national and international markets to earn profit.
2. Is sugarcane a cash crop?
Yes, sugarcane is one of the most important cash crops in India.
3. What are examples of cash crops?
Cotton, Jute, sugarcane, etc., are examples of cash crops.
4. What is the difference between cash crop farming and subsistence farming?
The major difference between cash crop farming and subsistence farming is that cash crops are grown for selling purposes to earn profits, whereas subsistence farming refers to the growing of crops for fulfilling basic needs and not for selling purposes.


Related Blogs












