Different Types of Soil in India and Their Characteristics

India has an extensive variety of soils. These range from rich, black soil in the Deccan plateau regions to sandy deserts in Rajasthan. In this blog, we'll gain an in-depth understanding of soil, including its formation, the factors that affect soil formation, and the various types of soil found in India.
Table of Contents
- What is 'Soil?'
- What are the Different Types of Soil in India?
- What is the Process of Soil Formation?
- What are the Five Major Factors Affecting Soil Formation?
- How 'Soil' Shapes Agriculture in India
What is ‘Soil?’
Soil is a valuable natural resource that forms the upper layer of the earth's mantle. It is a mix of minerals and organic matter (decayed plants and animals), which form the foundation of the earth's surface to support the growth of flora and fauna. The soil in its present form is the result of thousands of years of weathering and gradation of parent rock material. The properties of a soil are largely determined by the composition of the parent rock and the climate of a particular region.
Some of the major components of soils are:
- Organic matter – decomposed plants and animals.
- Inorganic matter – minerals and rock debris derived from parent rocks.
- Water
- Air
Different types of soil contain these ingredients in different amounts. Some soils are abundant in one or more of these, while others may be deficient in one or more. Ideally, soil should have 50% solid material and 50% pore space. Even the pore spaces should consist of half air and half water.
What are the Different Types of Soil in India?
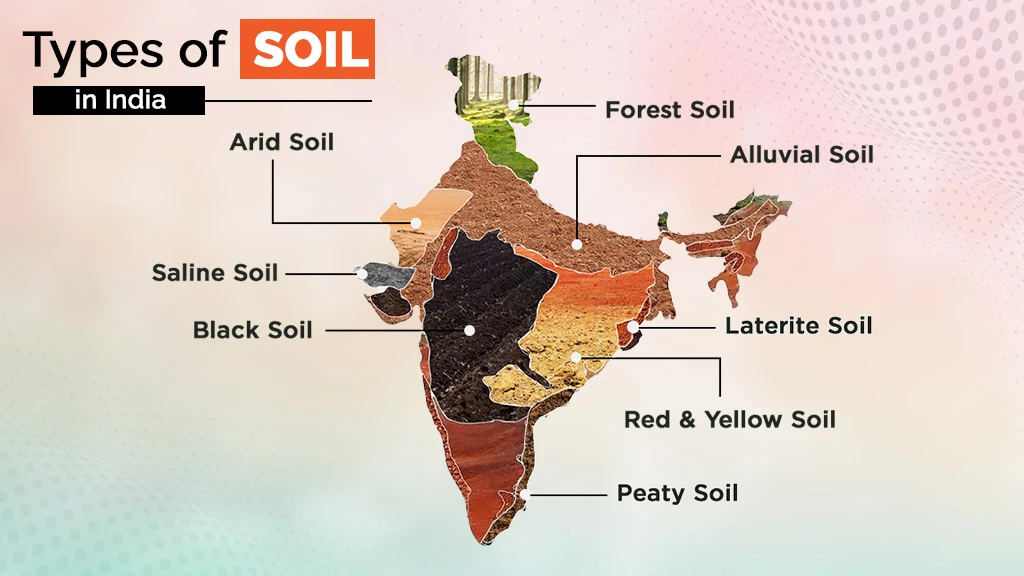
India has diverse landforms, climatic conditions, and vegetation. As a result, different types of soils are found in India. Adopting the scientific approach for soil classification after Independence, the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has given 8 major soil classifications based on genesis, colour, composition, and location.
We have given the soil type chart of the major soils of India below:
|
Type of Soil |
Characteristics |
Region |
Crops Grown |
|
Alluvial Soil |
- Formed through transportation and deposition of sediments carried by winds, rivers, or glaciers. - Forms 40% of India's land. - Most fertile soil. |
Indo-Gangetic region from Rajasthan to West Bengal and East Coast |
Wheat, maize, sugarcane, pulses, millet |
|
Black Soil |
- Also called regur soil or black cotton soil. - Formed through the weathering of igneous rocks. - Forms 15% of India's land. - Most mature soil, rich in magnesium and calcium. |
Deccan Plateaus regions of Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, and MP |
Cotton, millet, maize, pulses, citrus fruits |
|
Red & Yellow Soil |
- Formed on metamorphic and crystalline rocks. - Due to high iron content, they appear red and turn yellow when hydrated. - Poor in nitrogen, phosphorus, and humus.
|
Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Chhattisgarh |
Wheat, oilseed, tobacco, pulses |
|
Laterite Soil |
- The word laterite is derived from the Latin word 'Later', meaning brick. - Accounts for 3.7% of India's land. - Deficient in organic matter, nitrogen, phosphate, and calcium. - Red in colour due to the presence of iron and aluminum. |
Odisha, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh, Assam |
Suitable for tree crops like Cashew nuts. |
|
Arid Soil |
- Also called desert soils. - They form 4.42% of India's land. - They are sandy and have low moisture content. - They have high salt content. |
Western Rajasthan, Southwest Haryana, Parts of Gujarat |
Bajra, jowar, green gram, black gram |
|
Saline Soil |
- Also called Usara or infertile soils. - High presence of sodium, potassium, and magnesium. - They do not support vegetative growth. - Gypsum or lime can be added to reclaim the soil. |
Rann of Kutch in Gujarat, East Coast delta, Sunderbans in West Bengals |
Suitable for growing leguminous crops such as green grams and beans. |
|
Forest Soil |
- They are formed in forests where rainfall is sufficient. Also called Mountain Soils. - Loamy and silty on valley sides and coarse-grained on the upper slope. - In the Himalayas, they are acidic with low humus content, but soils in lower valleys are fertile. |
Himalayan region, Western Ghats, and Eastern Ghats |
Temperate fruits, tea, coffee, and spices. |
|
Peaty Soil |
- Rich in organic matter and humus. - They are heavy and black in colour.
|
Found in regions of heavy rainfall and high humidity, such as the coastal areas of Bengal, Odisha, and Tamil Nadu. |
Jute, Rice, and Rubber |
What is the Process of Soil Formation?
The soil formation process, also known as pedogenesis, is a series of interrelated physical, chemical, biological, and climatic activities that transform parent rock material into finer soil particles that we see today.
The soil forms through three important processes – weathering, accumulation of organic matter, and translocation.
Weathering
The first step of soil formation is weathering. It is the process of breaking down parent rock materials through physical and chemical processes into smaller particles.
Physical weathering is the mechanical breakdown of parent rock materials into smaller materials due to changes in temperatures, pressures, and wind.
Chemical weathering is the decomposition of rocks through chemical reactions. It happens when minerals within rocks change their chemical composition due to gases in the atmosphere and water.
Accumulation of Organic Matter
Organic matter consists of dead plants and animals, which, upon decomposition, form humus. This process is also known as humification.
Translocation
It involves the movement of soil constituents like minerals and organic matter within the soil profile (vertical classification of soil) or between the horizons. Translocation of soil happens through the process of leaching and illuviation.
What are the Five Major Factors Affecting Soil Formation?
Five major factors affecting soil formation are: physical relief, parent rock material, climate, biological activity, and time. Let's briefly examine how these factors influence soil formation.
- Physical Relief (Topography): The shape and direction of land affect soil formation. Flat land surfaces, like Indo-Gangetic plains, have deeper fertile soils, whereas slopes have fewer deeper soils.
- Parent Rock Material: The weathering of the parent material is the main source of soil formation. Thus, the nature of the parent rock determines the colour, composition, and fertility of the soil. For instance, black soil is the result of the weathering of lava rocks of the Deccan Plateaus.
- Climate: Rain and temperature determine the pace with which the parent rock will break, the extent of soil development, and the composition of the soil.
- Time: Soil formation is a dynamic and long-term process. The time determines the maturity and profile development of the soil.
- Biological Activity: Organic matter, such as decomposed plants and animals, helps determine the soil's structure and composition.
Besides, human activities also influence the formation of soils.
How ‘Soil’ Shapes Agriculture in India?
Soil plays a critical role in increasing agricultural productivity. That is why knowledge of soil type, texture, composition, fertility, etc., is essential. In India, alluvial, black, and red soils together cover more than 75% of the land area. These soils are predominantly found in regions like the Indo-Gangetic plains, the Deccan plateau, and the eastern coastal belt—areas that also host the country’s leading agricultural states. Additionally, adoption of modern farming techniques and advanced machinery, such as tractors and specialized farm implements, has further improved soil quality through better ploughing and land preparation practices.
In addition to these major soil types, other varieties like arid, saline, peaty, forest, and laterite soils are also present in these regions, contributing to the agricultural success of India’s top farming states.
Frequently Asked Questions On Different Types of Soil in India and Their Characteristics
1. How many types of soil are there?
Soils in India have been classified into eight major types, namely, alluvial soil, black soil, red & yellow soil, laterite soil, arid soil, forest soil, saline soil, and peaty soil.
2. What types of plants grow in sandy soil?
Sandy soil is ideal for growing cucumbers, watermelons, and muskmelons.
3. Which type of soil has the highest water-holding capacity?
Clayey soil has the highest water storage capacity.
4. Which type of soil is the most porous?
Clayey soils have the highest porosity.


Related Blogs












