Urban Farming in India – Types, Advantages & Future

Urban farming in India plays a crucial role in ensuring food security for urban areas. It involves the cultivation, processing, and distribution of food in and around urban and peri-urban areas. This farming method reduces the longer transportation time and carbon emissions by promoting a sustainable farming approach in the limited spaces of the cities. It involves cultivating vegetables, fruits, and herbs in city spaces, such as rooftops or balconies, with the primary aim of personal consumption. The different types of urban farming are kitchen gardening, vertical farming, rooftop farming, etc. Go through the article to learn more about the benefits, challenges, and future of urban farming in India.
Table of Contents
- Overview of Urban Farming
- What are the Major Crops Cultivated in Urban Agriculture?
- What are the Different Types of Urban Farming?
- What are the Advantages of Urban Farming?
- What are the Challenges related to Urban Farming in India?
- Future of Urban Farming in India
Overview of Urban Farming
Urban farming or urban agriculture is the practice of cultivating, processing, and marketing food products within urban spaces. Urban farming involves different types of farming, such as kitchen gardening, rooftop farming, and vertical farming. The population in urban areas is on the rise, and so is the demand for food and food products.
The urban agriculture market was valued at around Rs. 18,64,541 crores in 2023. It is expected to grow at around 3.1% annually to reach Rs. 23,98,118 crores by 2030. In recent years, urban farming has gained importance in India. Urban agriculture offers an innovative approach to deal with the challenges related to food in urban spaces, where the land is limited, and demand for sustainable food production is high.
Urban farming is being practiced in many Indian cities, like Chennai, Mumbai, Kolkata, Delhi, and Bengaluru. As it is gaining traction across the country, state governments have begun to take up initiatives to promote urban farming. In 2021, the Bihar government started to pay input expenses in 5 smart cities. In 2014, Tamil Nadu developed a "do-it-yourself" kit under the Urban Horticulture Development Scheme to help the public grow a variety of vegetables in their houses, apartment buildings, and houses.
What are the Major Crops Cultivated in Urban Agriculture?
Urban agriculture allows the cultivation of vegetables with a short production cycle. Some of the vegetables cultivated in urban farming are harvested within sixty days of their plantation, making them an ideal option. Urban farming aims to produce vegetables and fruits that are highly valued and in high demand. Some of the major crops cultivated in urban agriculture are:
- Root crops: Sweet Potato, Potato, Radish, Cassava, Carrot, Ginger, among others.
- Vegetables: Capsicum, Brinjal, Tomato, Chillies, and others.
- Fruits: Mangoes, Bananas, Guava, Avocados, Cherry, Citrus, Coconut, etc.
- Mushrooms: Oyster mushroom, Paddy straw mushroom, Button mushroom, and others.
- Herbs or green leafy vegetables: Curry leaves, Watercress, Coriander, Spinach, and others.
What are the Different Types of Urban Farming?
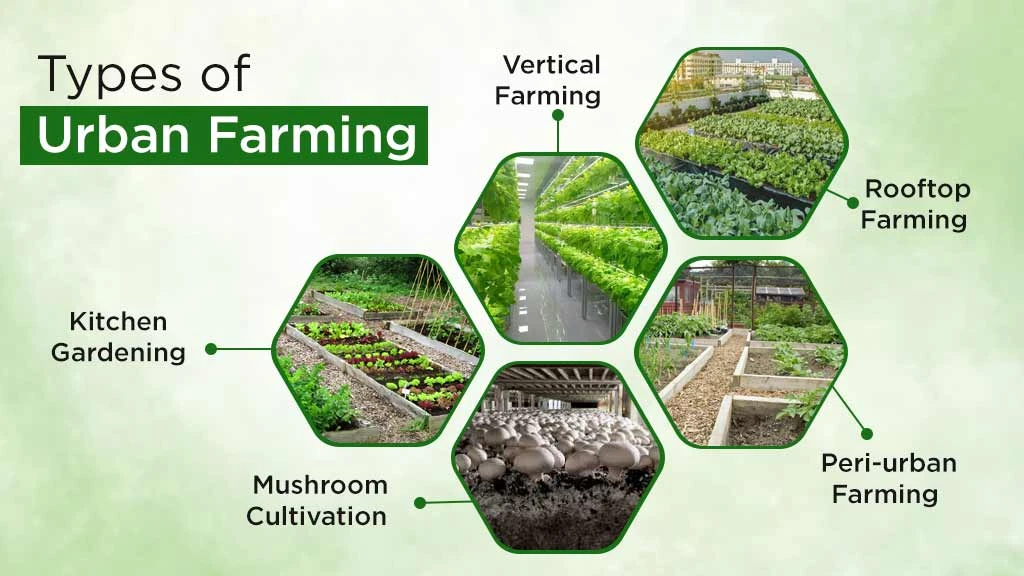
Different types of urban farming are practised in India. Depending on the size, area, produced item, and several other aspects. Some of the popular types of urban farming are as follows:
- Kitchen Gardening
- Vertical Farming
- Terrace & Roof Garden
- Peri-urban Farming
- Urban Beekeeping
Kitchen Gardening
This type of urban farming involves the cultivation of herbs, fruits, and vegetables that are commonly used in the kitchen. These are cultivated in and around the domestic area on a limited scale. A 250-square-meter plot is enough for growing vegetables for a five-member family. The food products are cultivated with the objective of being used for household purposes only and not for commercial purposes. This type of urban farming allows less dependency on the market availability of the cultivated vegetables or herbs. Also, kitchen gardening is a fun and healthy hobby for both old and young.
Vertical Farming
Vertical farming is another type of urban farming that involves crop cultivation in stacked layers. Vertical farming offers higher yields in specific areas than other forms of farming. Abandoned old buildings, tall apartments, or walls can be used for this type of farming to increase the area covered for vegetable cultivation. Vertical structures can be developed using different materials, including used plastic bottles, simple bamboo, and PVC pipes.
Terrace & Roof Garden
Rooftop farming, as the name suggests, is a farming performed on the rooftop of an apartment or a house. It can be practised by individuals or a group of families. This farming is done to meet the cultivated product needs of families or communities involved in the cultivation. The objective here is to use the empty space for cultivation to reduce market dependency on the cultivated product. Unused containers can be used to grow herbs, flowers, vegetables, and fruits on terraces. Also, plants are grown in grow bags, self-watering pots, iron supports, and wooden benches. Polyhouses and shade nets can be employed as protective structures.
Peri-Urban Farming
Peri-Urban agriculture refers to farming performed at the perimeter or outskirts of urban space. Here, the farmers are free to practice large-scale production. In India, over 65% of the produce available in the urban market is from peri-urban farming. This practice helps reduce the cost involved in transportation, mediators, and commissions. The crops cultivated in this type of urban farming involve leafy vegetables, fruits, and herbs that remain fresh for consumption due to the shorter distance.
Urban Beekeeping
Urban beekeeping involves raising bee colonies in urban gardens or peri-urban regions for purposes of pollination and honey production. Apiculture helps produce a variety of bee products, including honey and beeswax. A large population in highly crowded urban regions takes up urban beekeeping as a hobby. Bee colonies can be raised in rooftop gardens and peri-urban regions for increased yield via pollination.
What are the Advantages of Urban Farming?
The main advantages of urban farming include nutritional food, social well-being, environmental benefits, economic benefits, and efficient resource utilisation.
- Nutritional food: Urban farming allows the cultivation of fruits and vegetables that are rich in minerals and vitamins and offer necessary nutrients.
- Environmental benefits: The reduced use of water, space, and material involved in urban farming impacts the environment relatively less than traditional farming.
- Social well-being: Urban farming performed on community land increases social interaction as people can share their cultivation with others, leading to improved social well-being.
- Economic benefits: Urban farming allows employment opportunities to marginal individuals, thus providing them with a good income.
- Efficient resource utilisation: With limited land and resources to cultivate, only the interested individual can utilise the space available, thus improving the efficient use of resources.
What are the Challenges related to Urban Farming in India?
The primary challenges related to urban farming in India include limited land availability, regulatory issues, water resource management, and soil pollution.
- Land scarcity is the main issue plaguing urban farming in India. There is a lack of open spaces due to rapid urbanization. Thus, the scope of large-scale farming is limited, which also limits higher yields and crop varieties that can be cultivated.
- Urban planning and agricultural policy do not give due consideration to urban farming in the agricultural production chain. Also, it can be challenging to comply with the regulations placed for urban farming, including zoning regulations and securing permits.
- Urban farming demands effective water management because of huge water scarcity in several cities. Thus, there is a need for responsible water use practices and efficient irrigation systems to ensure sustainable urban farming.
- This farming can pose health and environmental risks due to contamination of soil and water. Water sources can get contaminated due to improper use of raw organic manure, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- Soil contamination is a major issue in Indian cities due to improper waste disposal, pollution, and industrial activities. It can adversely impact crop quality while also posing health-related risks to consumers.
Future of Urban Farming in India
One of the most serious concerns is India’s rapidly growing urban population, along with ensuring its food and nutritional security. Urban farming is a viable solution to address the issue of food security in towns, large cities, and peri-urban areas. However, there is a need for an effective policy framework for urban farming in India to establish suitable legal, policy measures, and incentive mechanisms. India needs to rapidly adopt technologies like mobile co-farming platforms, aquaponics, soilless cultivation, and smart farming to boost urban farming. The path forward includes public-private partnerships and integration into urban planning to ensure a resilient and self-sufficient future.
Frequently Asked Questions On Urban Farming in India – Types, Advantages & Future
1. What is urban farming?
Urban farming is cultivating, processing, and marketing food products within urban spaces.
2. What are urban and peri-urban farming?
Urban farming is performed within the city, whereas peri-urban farming is practised at the perimeter or outskirts of the city.
3. How can urban farming help communities?
Urban farming helps communities by improving the availability of fresh and healthy food. The involvement of people in urban farming in community lands improves social well-being.
4. Is urban farming profitable?
Yes, urban farmers can gain significant profit from the cultivated produce.
5. Is urban farming sustainable?
Urban farming is sustainable as it reduces the excessive use of resources such as water and land.
6. Why is urban farming important?
Urban farming fosters and promotes a sustainable and local food system and ensures food security in the urban region.


Related Blogs












